Volume 2, Number 3—July 1996
Dispatch
Two Morbilliviruses Implicated in Bottlenose Dolphin Epizootics
Figure
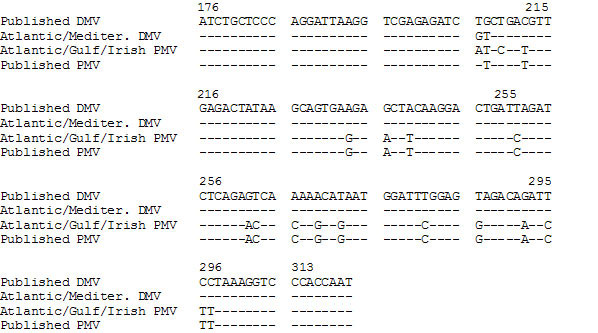
Figure. Partial nucleotide sequence of DMV and PMV morbillivirus P gene compared with published DMV and PMV sequences (12). Primer sequences used were 5'-ATC TGC TCC CAG GAT TAA GGT CGA-3' (forward) and 5'-CGG GAT TGG TGG GAC CTT TA-3' (reverse). RT- PCR was performed (11). PCR products were cycle sequenced (20) or cloned into PDK101 (21) and sequenced by using T7 Sequenase (Amersham Corporation, Arlington Heights, IL) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
References
- Diallo A. Morbillivirus group: genome organization and proteins. Vet Microbiol. 1990;23:15563.
- Haas L, Subbarao SM, Harder T, Liess B, Barrett T. Detection of phocid distemper virus RNA in seal tissues using slot hybridization and the polymerase chain reaction amplification assay: genetic evidence that the virus is distinct from canine distemper virus. J Gen Virol. 1991;72:825–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Osterhaus ADME, Groen J, Spijkers HEM, Broeders HWJ, UytdeHaag FGCM, de Vries P, . Mass mortality in seals caused by a newly discovered virus-like morbillivirus. Vet Microbiol. 1990;23:343–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McCullough SJ, McNeilly F, Allan GM, Kennedy S, Smyth JA, Cosby SL, . Isolation and characterization of a porpoise morbillivirus. Arch Virol. 1991;118:247–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Osterhaus ADME, Visser IKG, de Swart RL, van Bressem MF, van de Bildt MWG, Örvell C, Morbillivirus threat to Mediterranean monk seals? Vet Rec. 1992;130:141–2.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Domingo M, Ferrer L, Pumarola M, Marco A, Plana J, Kennedy S, . Morbillivirus in dolphins. Nature. 1990;348:21.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Van Bressem MF, Visser IKG, de Swart RL, Örvell C, Stanzani L, Androukaki E, . Dolphin morbillivirus infection in different parts of the Mediterranean Sea. Arch Virol. 1993;129:235–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lipscomb TP, Schulman FY, Moffett D, Kennedy S. Morbilliviral disease in Atlantic bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from the 1987-88 epizootic. J Wildl Dis. 1994;30:567–71.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schulman FY, Lipscomb TP, Moffett D, Krafft AE, Lichy JH, sai MM, et al. Reevaluation of the 1987-88 Atlantic coast bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) mortality event with histologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular evidence for a morbilliviral etiology. In preparation, 1996.
- Lipscomb TP, Kennedy S, Moffett D, Ford BK. Morbilliviral disease in an Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) from the Gulf of Mexico. J Wildl Dis. 1994;30:572–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Krafft AE, Lichy JH, Lipscomb TP, Klaunberg BA, Kennedy S, Taubenberger JK. Postmortem diagnosis of morbillivirus infection in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico Epizootics by a polymerase chain reaction-based assay. J Wildl Dis. 1995;31:410–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barrett T, Visser IKG, Mamaev L, Goatley L, van Bressem MF, Osterhaus ADME. Dolphin and porpoise morbilliviruses are genetically distinct from phocine distemper virus. Virology. 1993;193:1010–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lipscomb TP, Kennedy S, Moffett D, Krafft AE, Klaunberg BA, Lichy JH, Morbilliviral epizootic in Atlantic bottlenose dolphins of the Gulf of Mexico. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1996. In press.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Visser IKG, van Bressem MF, de Swart RL, van de Bildt MWG, Vos HW, van der Heijden , RWJ, . Characterization of morbilliviruses isolated from dolphins and porpoises in Europe. J Gen Virol. 1993;74:631–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kenney RD. Bottlenose dolphins off the northeastern United States. In: Leatherwood S, Reeves RR, editors. The bottlenose dolphin. San Diego: Academic Press, 1990:369-86.
- Breslow NE, Day NE. Statistical methods in cancer research.Vol. 1 Lyon, France. International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1980.
- Geraci JR. Clinical investigation of the 1987-88 mass mortality of bottlenose dolphins along the US central and south Atlantic coast: final report to National Marine Fisheries Service and U.S. Navy. Guelph, Canada: Office of Naval Research, and Marine Mammal Commission; 1989.
- Duignan PJ, House C, Geraci JR, Duffy N, Rima BK, Walsh MT, Morbillivirus infections in cetaceans of the western Atlantic. Vet Microbiol. 1995;44:241–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Duignan PJ, House C, Geraci JR, Early G, Copland H, Walsh MT, Morbillivirus infection in two species of pilot whales (Globicephala sp.) from the western Atlantic. Mar Mamm Sci. 1995;11:150–62. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Reid AH, Tsai MM, Venzon DJ, Wright CF, Lack EE, O'Leary TJ. MDM2 amplification, P53 mutation, and accumulation of the P53 gene product in malignant fibrous histiocytoma. Diagn Mol Pathol. 1996;5:65–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kovalic D, Kwak JH, Weisblum B. General method for direct cloning of DNA fragments generated by the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991;19:4560. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: December 20, 2010
Page updated: December 20, 2010
Page reviewed: December 20, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.