Volume 20, Number 10—October 2014
Dispatch
Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, South Korea, 2013
Figure 1
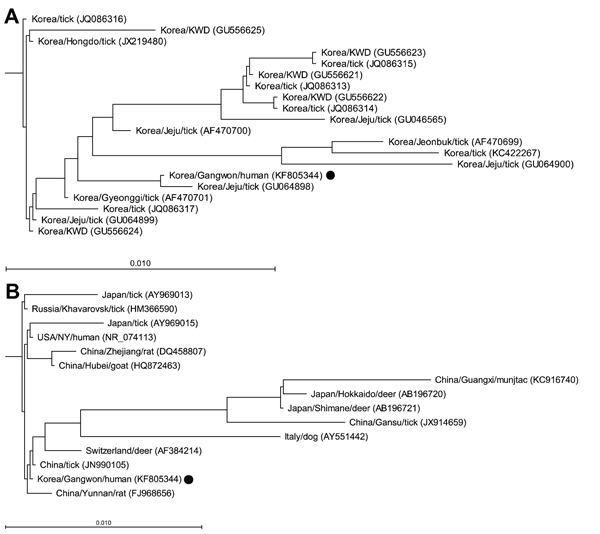
Figure 1. Phylogenetic trees for partial 16S rRNA gene sequences of an Anaplasma phagocytophilum isolate obtained from a patient with human granulocytic anaplasmosis in South Korea (black dots) and those of the A. phagocytophilum strains reported from A) South Korea and B) other countries. Trees were constructed by using the neighbor-joining method. Locations (country/province or city), hosts, and GenBank accession numbers are indicated. Branch lengths of trees show evolutionary distances. Scale bars indicate 1.0% sequence distance. KWD, Korean water deer.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: September 22, 2014
Page updated: September 22, 2014
Page reviewed: September 22, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.