Volume 20, Number 12—December 2014
Dispatch
Prevalence of SFTSV among Asian House Shrews and Rodents, China, January–August 2013
Figure
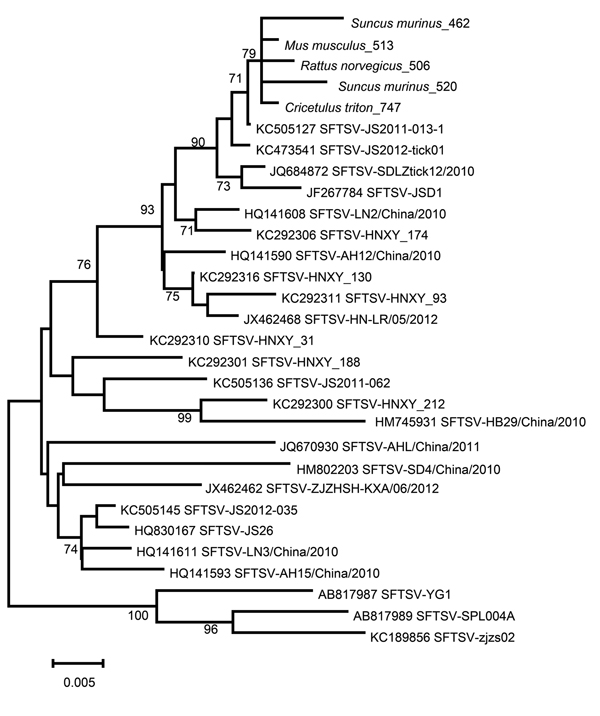
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) amplified from the spleens of Asian house shrew and rodents. The neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree was constructed by using MEGA 5.2 software(http://www.megasoftware.net/).GenBank accession numbers precede isolate names on the right side of the figure. Numbers at nodes represent bootstrap values. Scale bar represents nucleotide substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: November 19, 2014
Page updated: November 19, 2014
Page reviewed: November 19, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.