Volume 20, Number 2—February 2014
Research
Genomic Variability of Monkeypox Virus among Humans, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Figure 1
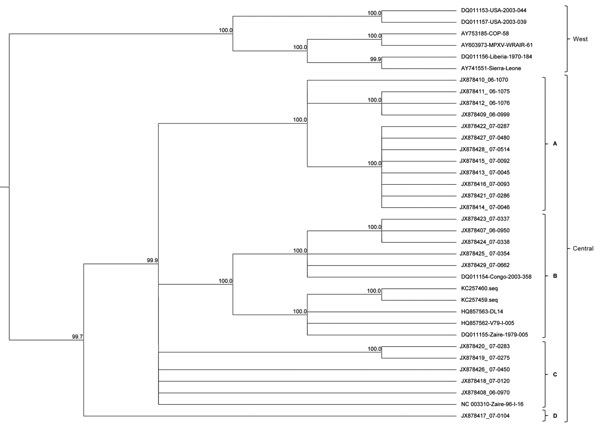
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of whole-genome direct sequencingEvolutionary relationships between sequenced samples and archived monkeypox virus (MPXV) sequences were determined for the central coding region sequence (MPXV nucleotide positions ≈56000–120000)A cladogram representing the topology of an unrooted Bayesian phylogenetic reconstruction is shown for samples identified by sample number and/or GenBank accession numberThe Central and Western African clades and the 4 distinct lineages are indicatedConfidence values for branching events were computed by Markov chain Monte Carlo convergenceNumbers at nodes represent Bayesian posterior probabilities computed by using MrBayes 3.1.2 (30).
References
- Moss B. Poxviridae: The viruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM. Field's Virology, 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven 2001. pp. 2849–83.
- Chen N, Li G, Liszewski MK, Atkinson JP, Jahrling PB, Feng Z, Virulence differences between monkeypox virus isolates from West Africa and the Congo basin. Virology. 2005;340:46–63. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Emerson GL, Li Y, Frace MA, Olsen-Rasmussen MA, Khristova ML, Govil D, The phylogenetics and ecology of the orthopoxviruses endemic to North America. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e7666. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Esposito JJ, Sammons SA, Frace AM, Osborne JD, Olsen-Rasmussen M, Zhang M, Genome sequence diversity and clues to the evolution of variola (smallpox) virus. Science. 2006;313:807–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gubser C, Hue S, Kellam P, Smith GL. Poxvirus genomes: a phylogenetic analysis. J Gen Virol. 2004;85:105–17 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Werden SJ, Rahman MM, McFadden G. Poxvirus host range genes. Adv Virus Res. 2008;71:135–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hendrickson RC, Wang C, Hatcher EL, Lefkowitz EJ. Orthopoxvirus genome evolution: the role of gene loss. Viruses. 2010;2:1933–67. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Carroll DS, Emerson GL, Li Y, Sammons S, Olson V, Frace M, Chasing Jenner's vaccine: revisiting cowpox virus classification. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e23086. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Essbauer S, Pfeffer M, Meyer H. Zoonotic poxviruses. Vet Microbiol. 2010;140:229–36. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hansen H, Okeke MI, Nilssen O, Traavik T. Comparison and phylogenetic analysis of cowpox viruses isolated from cats and humans in Fennoscandia. Arch Virol. 2009;154:1293–302. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Henderson DA, Inglesby TV, Bartlett JG, Ascher MS, Eitzen E, Jahrling PB, Smallpox as a biological weapon: medical and public health management. Working Group on Civilian Biodefense. JAMA. 1999;281:2127–37. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hutin YJ, Williams RJ, Malfait P, Pebody R, Loparev VN, Ropp SL, Outbreak of human monkeypox, Democratic Republic of Congo, 1996 to 1997. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001;7:434–8 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jezek Z, Grab B, Paluku KM, Szczeniowski MV. Human monkeypox: disease pattern, incidence and attack rates in a rural area of northern Zaire. Trop Geogr Med. 1988;40:73–83 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jezek Z, Grab B, Szczeniowski M, Paluku KM, Mutombo M. Clinico-epidemiological features of monkeypox patients with an animal or human source of infection. Bull World Health Organ. 1988;66:459–64 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Meyer H, Perrichot M, Stemmler M, Emmerich P, Schmitz H, Varaine F, Outbreaks of disease suspected of being due to human monkeypox virus infection in the Democratic Republic of Congo in 2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:2919–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fuller T, Thomassen HA, Mulembakani PM, Johnston SC, Lloyd-Smith JO, Kisalu NK, Using remote sensing to map the risk of human monkeypox virus in the Congo Basin. EcoHealth. 2011;8:14–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Khodakevich L, Jezek Z, Messinger D. Monkeypox virus: ecology and public health significance. Bull World Health Organ. 1988;66:747–52 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Khodakevich L, Jezek Z, Kinzanzka K. Isolation of monkeypox virus from wild squirrel infected in nature. Lancet. 1986;1:98–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Khodakevich L, Szczeniowski M. Manbu-ma-Disuse, Jezek Z, Marennikova S, Nakano J, et al. The role of squirrels in sustaining monkeypox virus transmission. Trop Geogr Med. 1987;39:115–22.
- Rimoin AW, Mulembakani PM, Johnston SC, Lloyd Smith JO, Kisalu NK, Kinkela TL, Major increase in human monkeypox incidence 30 years after smallpox vaccination campaigns cease in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:16262–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Learned LA, Reynolds MG, Wassa DW, Li Y, Olson VA, Karem K, Extended interhuman transmission of monkeypox in a hospital community in the Republic of the Congo, 2003. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;73:428–34 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reed KD, Melski JW, Graham MB, Regnery RL, Sotir MJ, Wegner MV, The detection of monkeypox in humans in the Western Hemisphere. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:342–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hess M, Sczyrba A, Egan R, Kim TW, Chokhawala H, Schroth G, Metagenomic discovery of biomass-degrading genes and genomes from cow rumen. Science. 2011;331:463–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Elde NC, Child SJ, Eickbush MT, Kitzman JO, Rogers KS, Shendure J, Poxviruses deploy genomic accordions to adapt rapidly against host antiviral defenses. Cell. 2012;150:831–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shchelkunov SN, Totmenin AV, Babkin IV, Safronov PF, Ryazankina OI, Petrov NA, Human monkeypox and smallpox viruses: genomic comparison. FEBS Lett. 2001;509:66–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bahar MW, Graham SC, Chen RA, Cooray S, Smith GL, Stuart DI, How vaccinia virus has evolved to subvert the host immune response. J Struct Biol. 2011;175:127–34. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kulesh DA, Baker RO, Loveless BM, Norwood D, Zwiers SH, Mucker E, Smallpox and pan-orthopox virus detection by real-time 3′-minor groove binder TaqMan assays on the Roche LightCycler and the Cepheid Smart Cycler platforms. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:601–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kulesh DA, Loveless BM, Norwood D, Garrison J, Whitehouse CA, Hartmann C, Monkeypox virus detection in rodents using real-time 3′-minor groove binder TaqMan assays on the Roche LightCycler. Lab Invest. 2004;84:1200–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:1572–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Campbell JA, Trossman DS, Yokoyama WM, Carayannopoulos LN. Zoonotic orthopoxviruses encode a high-affinity antagonist of NKG2D. J Exp Med. 2007;204:1311–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shchelkunov SN, Totmenin AV, Safronov PF, Mikheev MV, Gutorov VV, Ryazankina OI, Analysis of the monkeypox virus genome. Virology. 2002;297:172–94 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wittek R, Moss B. Tandem repeats within the inverted terminal repetition of vaccinia virus DNA. Cell. 1980;21:277–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gubser C, Smith GL. The sequence of camelpox virus shows it is most closely related to variola virus, the cause of smallpox. J Gen Virol. 2002;83:855–72 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yang Z, Moss B. Interaction of the vaccinia virus RNA polymerase-associated 94-kilodalton protein with the early transcription factor. J Virol. 2009;83:12018–26. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Christen LA, Piacente S, Mohamed MR, Niles EG. Vaccinia virus early gene transcription termination factors VTF and Rap94 interact with the U9 termination motif in the nascent RNA in a transcription ternary complex. Virology. 2008;376:225–35. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nakazawa Y, Emerson GL, Carroll DS, Zhao H, Li Y, Reynolds MG, Phylogenetic and ecologic perspectives of a monkeypox outbreak, southern Sudan, 2005. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:237–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shchelkunov SN. How long ago did smallpox virus emerge? Arch Virol. 2009;154:1865–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tesh RB, Watts DM, Sbrana E, Siirin M, Popov VL, Xiao SY. Experimental infection of ground squirrels (Spermophilus tridecemlineatus) with monkeypox virus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:1563–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reynolds MG, Carroll DS, Karem KL. Factors affecting the likelihood of monkeypox's emergence and spread in the post-smallpox era. Curr Opin Virol. 2012;2:335–4.
1These authors are co–first authors.
2These authors contributed equally to this work.