Volume 20, Number 5—May 2014
Dispatch
Human Infections with Rickettsia raoultii, China
Figure
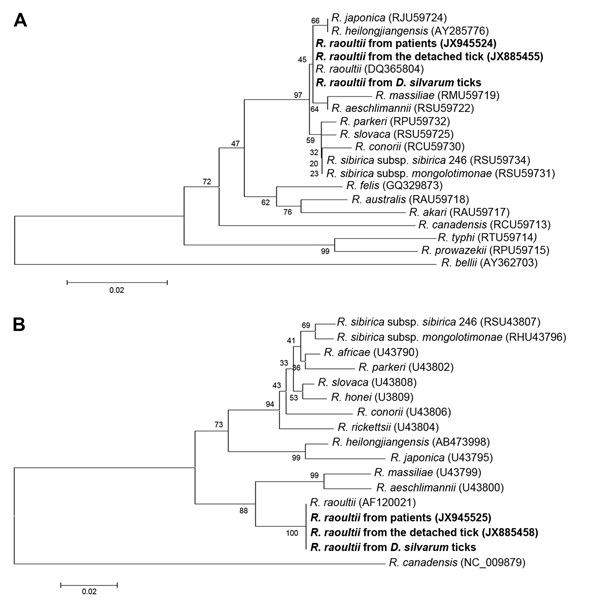
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of spotted fever group Rickettsia species, China, based on A) partial (341 bp) citrate synthase gene and B) partial (325 bp) 190-kDa outer membrane protein geneTrees were obtained by using the neighbor-joining method, distances were calculated by using Kimura 2-parameter analysis, and analysis was conducted by using Mega 5.0 software (www.megasoftware.net/)Nucleotide sequences determined in this study are indicated in boldfacePercentage of replicate trees in which associated taxa clustered in the bootstrap test (1,000 replicates) is shown to the left of each branchTrees are drawn to scale, and branch lengths have the same units as evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic treeGenBank accession numbers of sequences used in phylogenetic analysis are indicated in parenthesesScale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.