Volume 20, Number 6—June 2014
Dispatch
MERS Coronaviruses in Dromedary Camels, Egypt
Figure 1
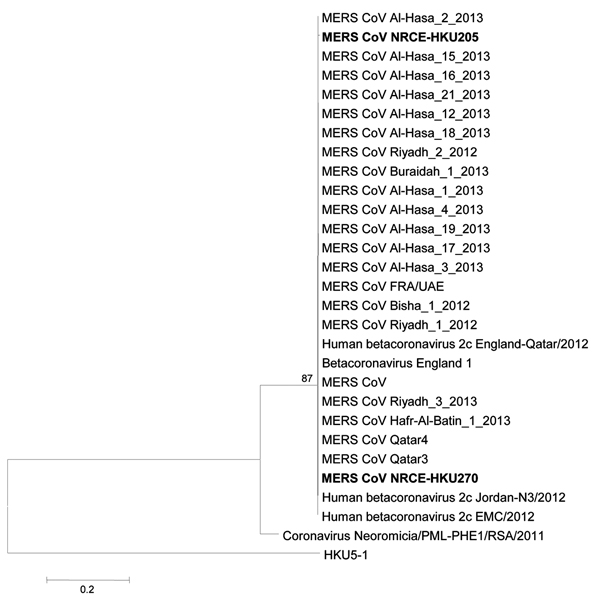
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analyses of a partial RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) sequence determined from samples from dromedary camels (Camelus dromedarius) NRCE-HKU205 and NRCE-HKU270 that were positive for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV)The viral RdRp region analyzed is a highly conserved region of the genome (covering motif B of RdRp) in nonstructural protein 12, at position 15202–15582 of MERS-CoV genomeThe partial RdRp sequence of NRCE-HKU205 (GenBank accession noKJ477102) and NRCE-HKU270 (GenBank accession noKJ477103) was aligned with human MERS-CoVs (GenBank accession nosKF600652, KF600630, KF600651, KF186567, KF600627, KF186564, KF600634, KF600632, KF600644, KF600647, KF600645, KF186565, KF186566, KF745068, KF600620, KF600612, KC667074, KC164505, KF192507, KF600613, KF600628, KF961222, KF961221, KC776174, and JX869059) and other representative animal betacoroanviruses (GenBank accession nosHKU5–1, EF065509; BtCoV/PML/Neo cfzul/RSA/2011, KC869678)Bat CoV HKU5–1 and bat CoV/PML/Neo cfzul/RSA/2011 were included in the analysis as outgroups because they are phylogenetically closest to MERS-CoVPhylogenetic trees were constructed by using MEGA5 (14) with neighbor-joining methodNumbers at nodes indicate bootstrap values determined by 500 replicatesOnly bootstrap values >70 are denotedBold type indicates MERS-CoV identified in the current studyScale bars indicate the estimated genetic distance of these viruses.
References
- World Health Organization. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) summary and literature update—as of 20 January 2014 [cited 2014 Feb 20]. http://www.who.int/csr/disease/coronavirus_infections/MERS_CoV_Update_20_Jan_2014.pdf
- Assiri A, McGeer A, Perl TM, Price CS, Al-Rabeeah AA, Cummings DAT, Hospital outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:407–16 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cotten M, Watson SJ, Kellam P, Al-Rabeeah AA, Makhdoom HQ, Assiri A, Transmission and evolution of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in Saudi Arabia: a descriptive genomic study. Lancet. 2013;382:1993–2002 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Annan A, Baldwin HJ, Corman VM, Klose SM, Owusu M, Nkrumah EE, Human betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012–related viruses in bats, Ghana and Europe. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:456–9 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ithete NL, Stoffberg S, Corman VM, Cottontail VM, Richards LR, Schoeman MC, Close relative of human Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in bat, South Africa. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:1697–9 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Memish ZA, Mishra N, Olival KJ, Fagbo SF, Kapoor V, Epstein JH, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in bats, Saudi Arabia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:1819–23 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reusken CBEM, Haagmans BL, Müller MA, Gutierrez C, Godeke G-J, Meyer B, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus neutralising serum antibodies in dromedary camels: a comparative serological study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:859–66 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Perera RA, Wang P, Gomaa MR, El-Shesheny R, Kandeil A, Bagato O, Seroepidemiology for MERS coronavirus using microneutralisation and pseudoparticle virus neutralisation assays reveal a high prevalence of antibody in dromedary camels in Egypt, June 2013. Euro Surveill. 2013;18:20574 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reusken CB, Ababneh M, Raj VS, Meyer B, Eljarah A, Abutarbush S, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) serology in major livestock species in an affected region in Jordan, June to September 2013. Euro Surveill. 2013;18:20662 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hemida MG, Perera RA, Wang P, Alhammadi MA, Siu LY, Li M, Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) coronavirus seroprevalence in domestic livestock in Saudi Arabia, 2010 to 2013. Euro Surveill. 2013;18:20659 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Meyer B, Müller MA, Corman VM, Reusken CBEM, Ritz D, Godeke G-D, Antibodies against MERS coronavirus in dromedary camels, United Arab Emirates, 2003 and 2013. Emerg Infect Dis [Internet]. 2014 Apr [cited 2014 Feb 22]. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Haagmans BL, Al Dhahiry SH, Reusken CB, Raj VS, Galiano M, Myers R, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in dromedary camels: an outbreak investigation. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:140–5 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chu DK, Leung CY, Gilbert M, Joyner PH, Ng EM, Tse TM, Avian coronavirus in wild aquatic birds. J Virol. 2011;85:12815–20 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–9 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.