Volume 20, Number 7—July 2014
Research
Population-Based Analysis of Invasive Fungal Infections, France, 2001–2010
Figure 2
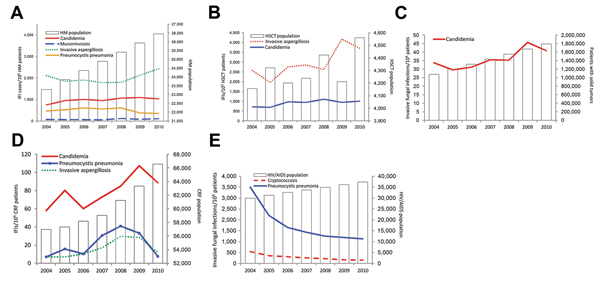
Figure 2. A) Invasive fungal infections in patients with hematologic malignancies (HM) in France, 2004–2010The case count continuously increased (p<0.001) over the periodCandidemia increased from 751.4 to 1,028.2 cases (+4.3%, p = 0.001), invasive aspergillosis (IA) from 2,112.4 to 2,434.2 cases (+2.7%, p = 0.002), and mucormycosis from 73.0 to 105.8 cases (+8.7%, p = 0.05) per 100,000 patients per yearInversely, the incidence of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (Pjp) decreased from 468.0 to 351.5 cases/100,000 patients/year (−4.4%, p = 0.006)B) In HSCT recipients (average 4,300 cases per year, no significant trend), candidemia increased from 721.5 to 1008.6 cases (+6.0%, p = 0.05) and invasive aspergillosis from 2,573.4 to 3,705.3 cases (+9.8%, p<0.001) per 100,000 HM patients per yearC) The number of patients with solid tumors continuously increased (p<0.001), and candidemia increased among those patients from 33.7 to 40.9 cases/100,000 patients/year (+6.2%, p<0.001)D) The number of patients with chronic renal failure continuously increased (p<0.001)Candidemia increased from 57.9 to 88.6 cases/100,000 patients/year (+8.1%), IA from 7.0 to 12.0 cases/100,000 patients/year (+18.4%, p = 0.007), and Pjp increased with a peak during 2007–2008 (+11.1%, p = 0.052)E) In the HIV/AIDS population (increase p<0.001), incidence of Pjp and cryptococcosis decreased by −17.9% and −19.0%, respectively (p<0.001)HSCT, hematologic stem cell transplant.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2These authors contributed equally to this article.