Volume 20, Number 7—July 2014
Letter
Stability of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus in Milk
Figure
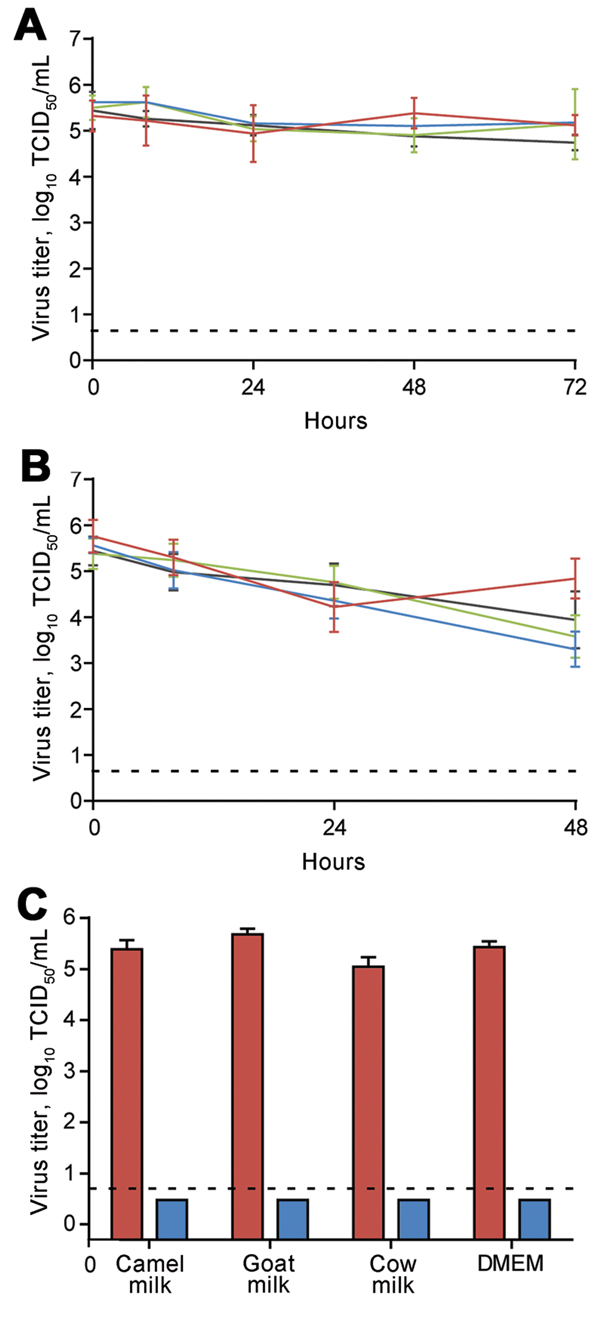
Figure. Viability of MERS-CoV in unpasteurized milkMERS-CoV strain Jordan-N3/2012 was diluted in milk or DMEM to a final TCID50 of 105.5/mL and stored at either 4°C (A) or 22°C (B)MERS-CoV titer was determined at 0, 8, 24, 48, and 72 hours post dilution in quintuplicateRed indicates dromedary camel milk; blue indicates goat milk; green indicates cow milk; black indicates DMEMC) Milk containing MERS-CoV was pasteurized by heating 1-mL aliquots of diluted virus at 63°C for 30 min in triplicateRed indicates unpasteurized; blue indicates pasteurizedInfectious virus titers were determined by endpoint titration on Vero E6 cells in triplicateDotted line depicts the detection limit of the assayMERS-CoV, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; TCID50, 50% tissue culture infective dose; DMEM, Dulbecco modified Eagle medium.