Volume 20, Number 8—August 2014
Dispatch
New Introductions of Enterovirus 71 Subgenogroup C4 Strains, France, 2012
Figure
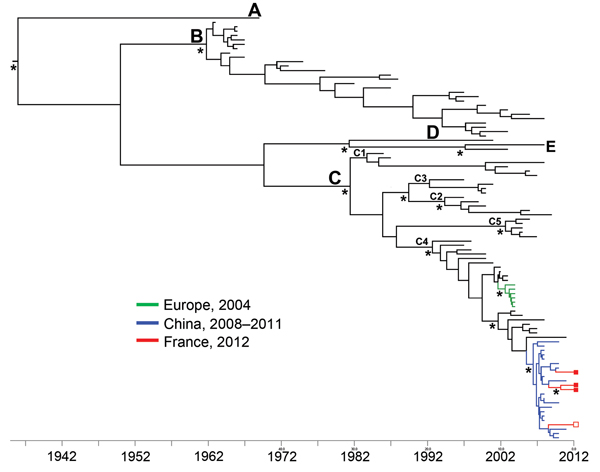
Figure. Dated phylogeny inferred by using 97 enterovirus 71 (EV-A71) 1D gene sequences encoding the VP1 capsid proteins (1DVP1)The dataset included the 4 sequences determined in this study; 37 sequences from EV-A71 C4 strains detected in Austria, China, Korea, France, Germany, Japan, and Taiwan during 1998–2011; and 57 sequences from prototype and clinical strains representative of the genogroups and subgenogroups A, B1–B5, C1–C5The tree topology shows the relationships between the strains isolated in France during 2012 and the strains circulating in ChinaThe x-axis represents sampling yearsThe phylogenetic relationships were inferred with complete 1DVP1 gene sequences (891 nt) by using a Bayesian method (BEAST software; http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk)The tree was reconstructed using FigTree 1.4.0 (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree)Asterisks at key nodes indicate posterior probability values >0.99Red indicates the 1DVP1 sequences determined in this study: complete sequences (GenBank accession nos.KF900159–61) are represented by closed squares on the right side of the figure; a partial sequence (298 nt) (GenBank accession no.KF900162) is represented by an open square)Green indicates the 1DVP1 sequences from EV-A71 C4 strains detected in France, Germany, and Austria in 2004Blue indicates the 1DVP1 sequences from EV-A71 C4 strains detected in China during 2008–2011Letters A–E indicate genogroups; C1–C4 indicate subgenogroups.