Volume 21, Number 11—November 2015
Research
No Geographic Correlation between Lyme Disease and Death Due to 4 Neurodegenerative Disorders, United States, 2001–2010
Figure
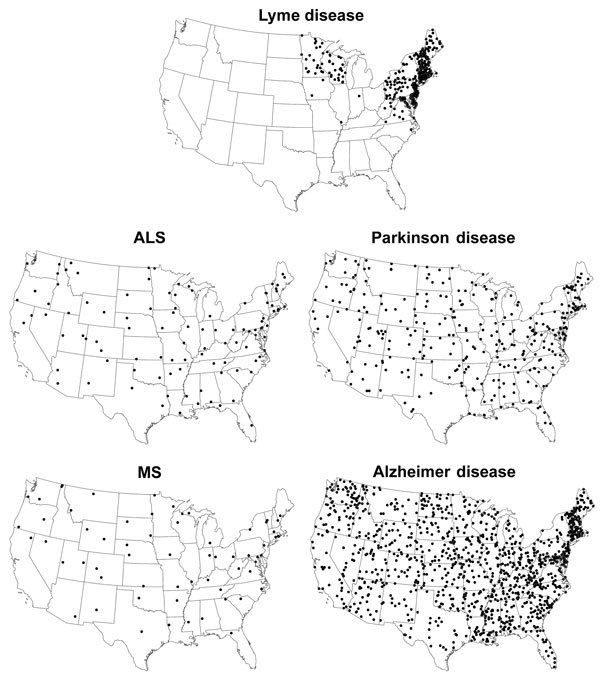
Figure. Geographic distribution of Lyme disease compared with that for deaths due to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), and Alzheimer disease. One dot represents 1 case (Lyme disease) or 1 death (ALS, Parkinson disease, MS, and Alzheimer disease) per 100,000 person-years; dots are placed randomly within the respective states.
1Current affiliation: Stanford University, Stanford, California, USA.
Page created: October 16, 2015
Page updated: October 16, 2015
Page reviewed: October 16, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.