Volume 21, Number 2—February 2015
Dispatch
Potentially Novel Ehrlichia Species in Horses, Nicaragua
Figure
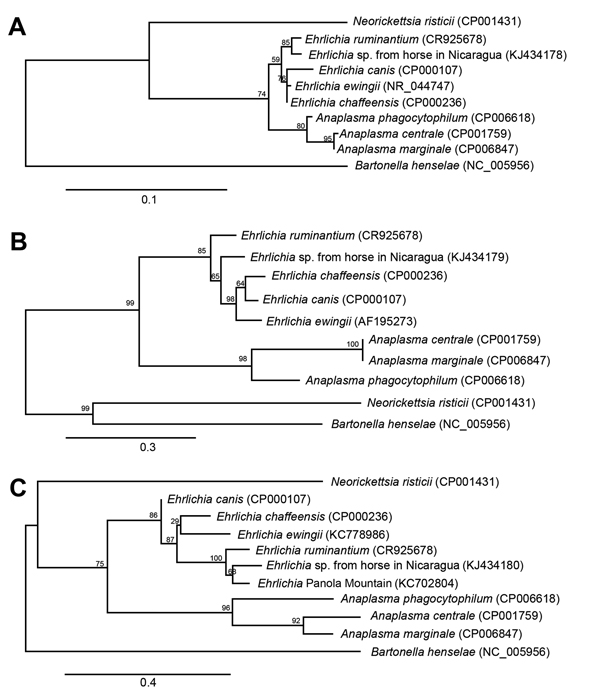
Figure. Phylogenetic trees of Ehrlichia sp. from horses in Nicaragua and selected bacterial species (GenBank accession numbers for reference sequences in parenthesis) based on partial sequences from genes coding for 16SrRNA (A), GroEL (B), and SodB (C). Sequences were aligned by using MUSCLE version 3.7 (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/muscle/), and alignments were refined by using Gblocks version 0.91b (http://www.idtdna.com/gblocks.com). Phylogenetic trees were constructed by using PhyML version 3.0 aLRT (http://code.google.com/p/phyml/) under the HKY85 model, and the resulting trees were rendered by using TreeDyn version 198.3 (http://www.treedyn.org/). Scale bars indicate number of substitutions per site, and the numbers in the branches represent percentage support of the node.