Volume 21, Number 2—February 2015
Dispatch
Cluster of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infections in Iran, 2014
Figure
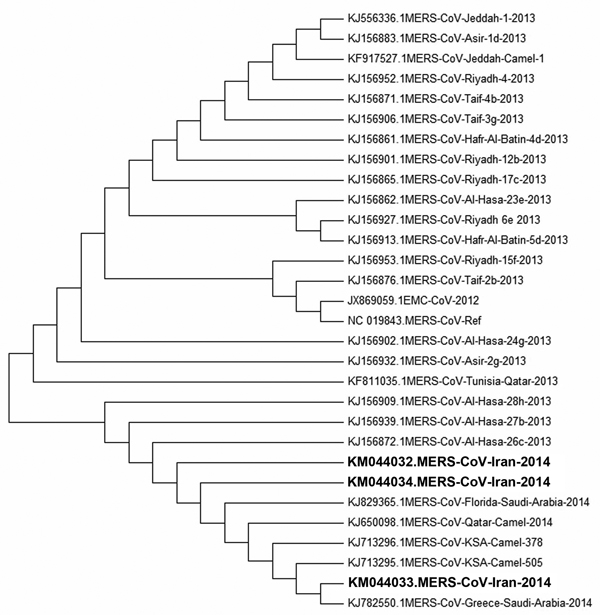
Figure. Phylogenic sequence analysis of 3 Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) isolates from patients in Kerman Province, Iran (boldface), 2014, compared with sequences from GenBank (accession numbers shown). MEGA 5.2 (http://www.megasoftware.net) was used for construction of neighbor-joining tree by using the Kimura 2-parameter model with uniform rates and 1,000 bootstrap replicates.
Page created: January 21, 2015
Page updated: January 21, 2015
Page reviewed: January 21, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.