Volume 21, Number 3—March 2015
Letter
Rickettsial Infections in Monkeys, Malaysia
Figure
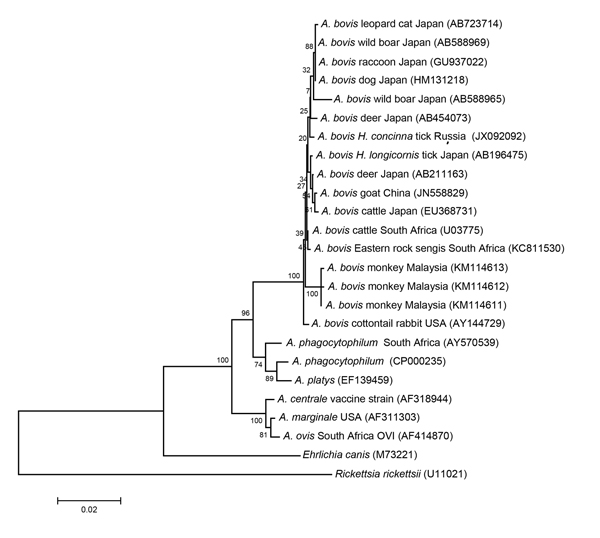
Figure. Phylogenetic relationships among various Anaplasma species, based on partial sequences of the 16S rRNA gene (1,263 bp). The dendrogram was constructed by using the neighbor-joining method in MEGA6 software (10) with the maximum composite likelihood substitution model and bootstrapping with 1,000 replicates. Rickettsia rickettsii (U11021) was used as an outgroup. Numbers in brackets are GenBank accession numbers. Representative Malaysian A. bovis sequences were deposited into the GenBank database under accession nos. KM114611–3. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Gumert MD. The common monkey of Southeast Asia: long-tailed macaque populations, ethnophoresy, and their occurrence in human environments. In: Fuentes A, Gumert M, Jones-Engel L, editors. Monkeys on the edge: ecology and management of long-tailed macaques and their interface with humans. Cambridge (UK): Cambridge University Press; 2011. p. 3–12.
- Maggi RG, Mascarelli PE, Balakrishnan N, Rohde CM, Kelly CM, Ramaiah L, “Candidatus Mycoplasma haemomacaque” and Bartonella quintana bacteremia in cynomolgus monkeys. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:1408–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tay ST, Mokhtar AS, Low KC, Mohd Zain SN, Jeffery J, Abdul Aziz N, Identification of rickettsiae from wild rats and cat fleas in Malaysia. Med Vet Entomol. 2014;28(Suppl 1):104–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Parola P. Rickettsia felis: from a rare disease in the USA to a common cause of fever in sub-Saharan Africa. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17:996–1000. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Odhiambo AM, Maina AN, Taylor ML, Jiang J, Richards AL. Development and validation of a quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assay specific for the detection of Rickettsia felis and not Rickettsia felis–like organisms. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014;14:476–81 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dumler JS, Barbet AF, Bekker CP, Dasch GA, Palmer GH, Ray SC, Reorganization of genera in the families Rickettsiaceae and Anaplasmataceae in the order Rickettsiales: unification of some species of Ehrlichia with Anaplasma, Cowdria with Ehrlichia and Ehrlichia with Neorickettsia, descriptions of six new species combinations and designation of Ehrlichia equi and ‘HGE agent’ as subjective synonyms of Ehrlichia phagocytophila. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:2145–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Krawczak FS, Nieri-Bastos FA, Nunes FP, Soares JF, Moraes-Filho J, Labruna MB. Rickettsial infection in Amblyomma cajennense ticks and capybaras (Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris) in a Brazilian spotted fever–endemic area. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:7.
- Parola F, Roux V, Camicas JL, Baradji I, Brouqui P, Raoult D. Detection of ehrlichiae in African ticks by polymerase chain reaction. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2000;94:707–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pinyoowong D, Jittapalapong S, Suksawat F, Stich RW, Thamchaipenet A. Molecular characterization of Thai Ehrlichia canis and Anaplasma platys strains detected in dogs. Infect Genet Evol. 2008;8:433–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:2725–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: February 18, 2015
Page updated: February 18, 2015
Page reviewed: February 18, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.