Volume 21, Number 4—April 2015
Dispatch
High Seroprevalence of Antibodies against Spotted Fever and Scrub Typhus Bacteria in Patients with Febrile Illness, Kenya
Figure 2
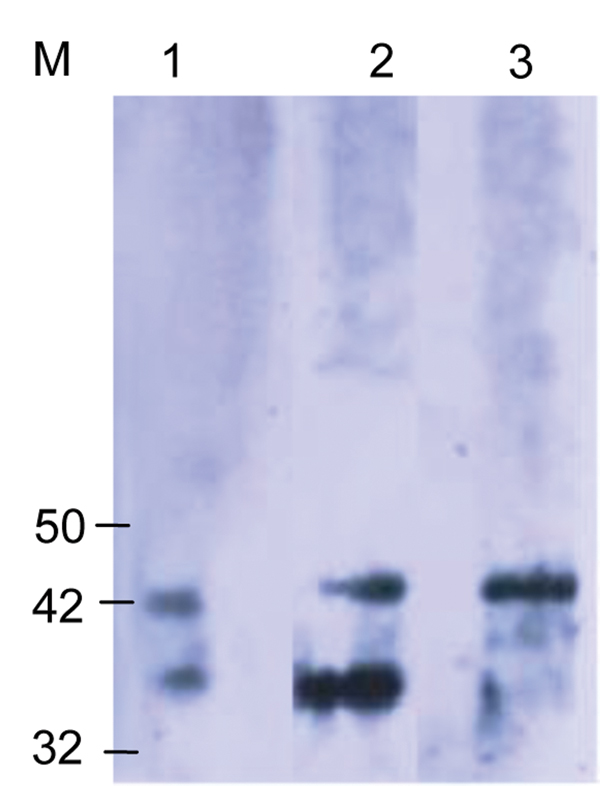
Figure 2. Western blot analysis using the Orientia spp.–specific antigen (Otr47b). Twenty scrub typhus reactive serum samples at a titer ≥1:6,000 were used. Negative controls were serum samples that were reactive to spotted fever and typhus group antigens. The scrub typhus reactive serum samples recognized the Otr47b antigen (lanes 2 and 3), but the spotted fever group and typhus group reactive serum samples did not (data not shown). Lane 1 was probed with a positive control serum sample from an earlier scrub typhus outbreak study (5). M, molecular mass standard, kDa.
References
- Raoult D, Fournier PE, Fenollar F, Jensenius M, Prioe T, de Pina JJ, Rickettsia africae, a tick-borne pathogen in travelers to sub-Saharan Africa. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1504–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- La Scola B, Raoult D. Laboratory diagnosis of rickettsioses: current approaches to diagnosis of old and new rickettsial diseases. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:2715–27.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Izzard L, Fuller A, Blacksell SD, Paris DH, Richards AL, Aukkanit N, Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:4404–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Richards AL, Jiang J, Omulo S, Dare R, Abdirahman K, Ali A, Human infection with Rickettsia felis, Kenya. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010;16:1081–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jiang J, Marienau KJ, May LA, Beecham HJ 3rd, Wilkinson R, Ching WM, Laboratory diagnosis of two scrub typhus outbreaks at Camp Fuji, Japan in 2000 and 2001 by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, rapid flow assay, and Western blot assay using outer membrane 56-kD recombinant protiens. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;69:60–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maina AN, Knobel DL, Jiang J, Halliday J, Feikin DR, Cleaveland S, Rickettsia felis infection in febrile patients, western Kenya, 2007–2010. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:328–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mutai BK, Wainaina JM, Magiri CG, Nganga JK, Ithondeka PM, Njagi ON, Zoonotic surveillance for rickettsiae in domestic animals in Kenya. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013;13:360–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Richards AL, Soeatmadji DW, Widodo MA, Sardjono TW, Yanuwiadi B, Hernowati TE, Seroepidemiologic evidence for murine and scrub typhus in Malang, Indonesia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;57:91–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Graf PC, Chretien JP, Ung L, Gaydos JC, Richards AL. Prevalence of seropositivity to spotted fever group rickettsiae and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in a large, demographically diverse US sample. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:70–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Prabhu M, Nicholson WL, Roche AJ, Kersh GJ, Fitzpatrick KA, Oliver LD, Q fever, spotted fever group, and typhus group rickettsioses among hospitalized febrile patients in northern Tanzania. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:e8–15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reller ME, Bodinayake C, Nagahawatte A, Devasiri V, Kodikara-Arachichi W, Strouse JJ, Unsuspected rickettsioses among patients with acute febrile illness, Sri Lanka, 2007. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:825–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bang HA, Lee MJ, Lee WC. Comparative research on epidemiological aspects of tsutsugamushi disease (scrub typhus) between Korea and Japan. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2008;61:148–50.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Balcells ME, Rabagliati R, Garcia P, Poggi H, Oddo D, Concha M, Endemic scrub typhus–like illness, Chile. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1659–63. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: March 17, 2015
Page updated: March 17, 2015
Page reviewed: March 17, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.