Volume 21, Number 4—April 2015
Research
Influenza A(H7N9) Virus Transmission between Finches and Poultry
Figure 2
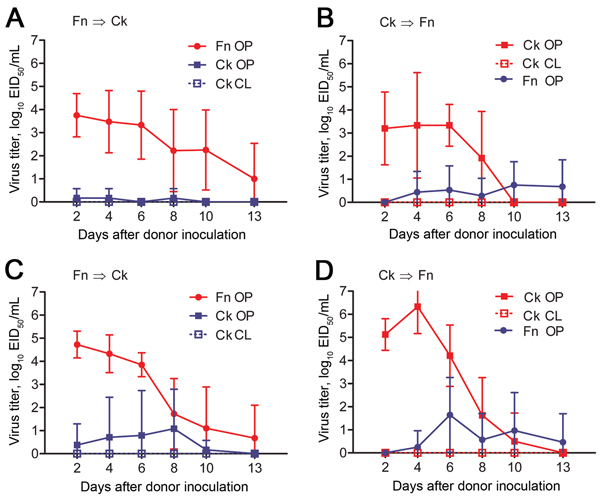
Figure 2. Waterborne transmission of virus between chicken and finches in an interspecies study of influenza A(H7N9) virus transmission. Finches (n = 8 or 10) and chickens (n = 6) were inoculated with strain A/Anhui/1/2013 (H7N9) (A, B) or A/chicken/Rizhao/867/2013 (H7N9) (C, D) and paired with naive birds in an environment in which physical contact was prevented but water was shared (Figure 1, panel A). Swab samples were obtained from birds every 48 h, and virus titers were determined in embryonated chicken eggs. Data are the average titer per time point ± SD. Directionality of transmission (i.e., infected → naive) is indicated in the top left of each panel. Red indicates infected animals; blue indicates naive animals. Ck, chicken; CL, cloacal swab sample; EID50, 50% egg infectious dose; Fn, finch; OP, oropharyngeal swab sample.