Volume 21, Number 6—June 2015
Dispatch
European Rabbits as Reservoir for Coxiella burnetii
Figure 1
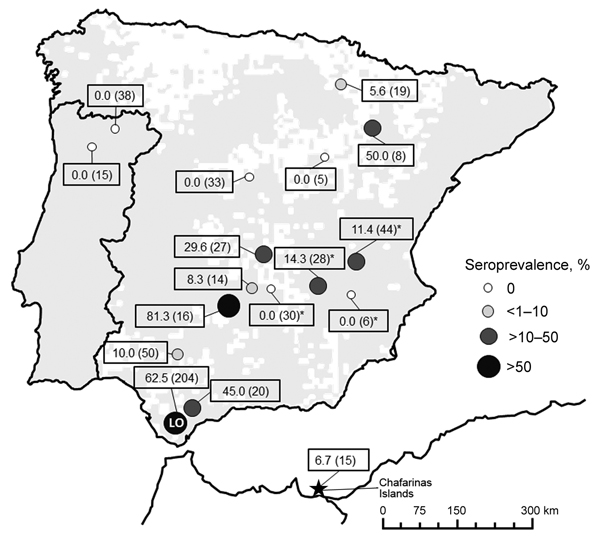
Figure 1. Seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii (sample size) in wild and farmed European rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus), Iberian Peninsula and Chafarinas Islands. The distribution area of wild rabbits in the Iberian Peninsula (10 x 10 km Universal Transverse Mercator squares) is shown (gray shading) according to Mitchel-Jones et al. (9). LO sampling location is indicated. *Rabbit farm.
References
- Ruiz-Fons F, Segalés J, Gortázar C. A review of viral diseases of the European wild boar: effects of population dynamics and reservoir role. Vet J. 2008;176:158–69. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Viana M, Mancy R, Biek R, Cleaveland S, Cross PC, Lloyd-Smith JO, Assembling evidence for identifying reservoirs of infection. Trends Ecol Evol. 2014;29:270–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ejercito CL, Cai L, Htwe KK, Taki M, Inoshima Y, Kondo T, Serological evidence of Coxiella burnetii infection in wild animals in Japan. J Wildl Dis. 1993;29:481–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ruiz-Fons F, Rodríguez O, Torina A, Naranjo V, Gortázar C, de La Fuente J. Prevalence of Coxiella burnetti infection in wild and farmed ungulates. Vet Microbiol. 2008;126:282–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Marrie TJ, Schlech WF, Williams JC, Yates L. Q fever pneumonia associated with exposure to wild rabbits. Lancet. 1986;1:427–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- González-Barrio D, Almería S, Caro MR, Salinas J, Ortiz JA, Gortazar C, Coxiella burnetii shedding by farmed red deer (Cervus elaphus). Transbound Emerg Dis. 2013.
- Monnerot M, Vigne JD, Biju-Duval C, Casane D, Callou C, Hardy C, Rabbit and man: genetic and historic approach. Genet Sel Evol. 1994;26:167–82. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Mitchell-Jones AJ, Amori G, Bogdanomicz W, Krystufek B, Beijnders PJ, Spitzenberger F, , editors. Atlas of European mammals. London: Academic Press; 1999.
- Maio E, Tania C, Balseiro A, Sevilla I, Romano A, Ortiz JA, Paratuberculosis in European wild rabbits from Iberian Peninsula. Res Vet Sci. 2011;91:212–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Berri M, Laroucau K, Rodolakis A. The detection of Coxiella burnetii from ovine genital swabs, milk and fecal samples by the use of a single touchdown polymerase chain reaction. Vet Microbiol. 2000;72:285–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Transactions on Automatic Control. 1974;19:716–25.
- Guatteo R, Beaudeau F, Joly A, Seegers H. Coxiella burnetii shedding by dairy cows. Vet Res. 2007;38:849–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Piñero A, Ruiz-Fons F, Hurtado A, Barandika JF, Atxaerandio R, García-Pérez AL. Changes in the dynamics of Coxiella burnetii infection in dairy cattle: an approach to match field data with the epidemiological cycle of C. burnetii in endemic herds. J Dairy Sci. 2014;97:2718–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Whitney EA, Massung RF, Candee AJ, Ailes EC, Myers LM, Patterson NE, Seroepidemiologic and occupational risk survey for Coxiella burnetii antibodies among US veterinarians. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:550–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: May 15, 2015
Page updated: May 15, 2015
Page reviewed: May 15, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.