Volume 22, Number 1—January 2016
Dispatch
Increased Risk for ESBL-Producing Bacteria from Co-administration of Loperamide and Antimicrobial Drugs for Travelers’ Diarrhea1
Figure
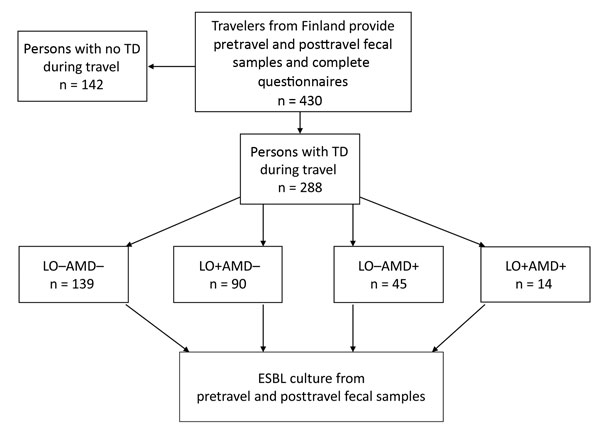
Figure. Study protocol for investigating risk for contracting ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae among travelers from Finland with TD. LO–AMD–, not treated with medication; LO+AMD–, treated with LO alone; LO–AMD+, treated with AMDs alone; LO+AMD+, treated with a combination of both drugs. AMD, antimicrobial drugs; ESBL, extended-spectrum β-lactamase; LO, loperamide; TD, travelers’ diarrhea.
1Preliminary results from this study were presented at the 13th Conference of the International Society of Travel Medicine (CISTM), May 24–28, 2015, Quebec City, Quebec, Canada.
Page created: December 18, 2015
Page updated: December 18, 2015
Page reviewed: December 18, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.