Volume 22, Number 1—January 2016
Dispatch
Seroepidemiology of Human Enterovirus 71 Infection among Children, Cambodia
Figure 1
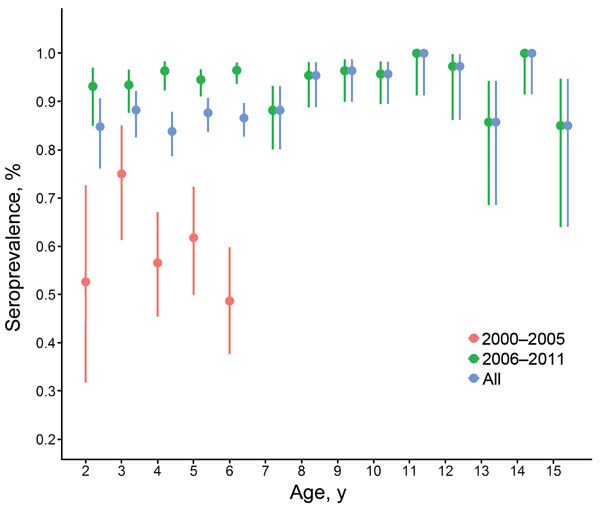
Figure 1. Age-associated seroprevalence of enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection in Cambodia, estimated by detection of EV71 seroneutralizing antibodies in inpatient children 2–15 years of age, 2000–2011. Error bars indicate 95% CIs. Serum samples were collected from routine national dengue surveillance in Cambodia.
Page created: December 18, 2015
Page updated: December 18, 2015
Page reviewed: December 18, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.