Reassortant Eurasian Avian-Like Influenza A(H1N1) Virus from a Severely Ill Child, Hunan Province, China, 2015
Wenfei Zhu
1, Hong Zhang
1, Xingyu Xiang
1, Lili Zhong, Lei Yang, Junfeng Guo, Yiran Xie, Fangcai Li, Zhihong Deng, Hong Feng, Yiwei Huang, Shixiong Hu, Xin Xu, Xiaohui Zou, Xiaodan Li, Tian Bai, Yongkun Chen, Zi Li, Junhua Li

, and Yuelong Shu

Author affiliations: National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing, China (W. Zhu, L. Yang, J. Guo, Y. Xie, X. Zou, X. Li, T. Bai, Y. Chen, Z. Li, Y. Shu); Key Laboratory for Medical Virology, National Health and Family Planning Commission, Beijing (W. Zhu, L. Yang, J. Guo, Y. Xie, X. Zou, X. Li, T. Bai, Y. Chen, Z. Li, Y. Shu); Hunan Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Changsha, China (H. Zhang, X. Xiang, F. Li, Z. Deng, Y. Huang, S. Hu, J. Li); Hunan Provincial People’s Hospital, Changsha (L. Zhong); Liuyang Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Liuyang, China (H. Feng, X. Xu)
Main Article
Figure 2
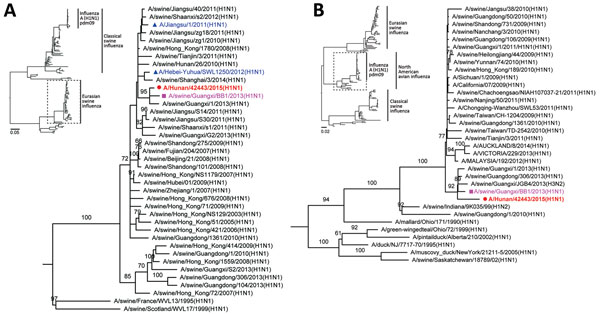
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of Eurasian avian-like influenza A/Hunan/42443/2015 virus (HuN EA-H1N1). A) Analysis of the hemagglutinin gene of representative clades of Eurasian avian-like H1N1 viruses. B) Analysis of the Polymerase basic 2 gene of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus. Insets show evolutionary analyses for all lineages of subtype H1N1 viruses. The reliability of the trees was assessed via bootstrap analysis with 1,000 replications; only bootstrap values >60% are shown. The horizontal distances are proportional to the genetic distance. Red indicates HuN EA-H1N1 virus, the virus reported in this study; pink indicates A/swine/Guangxi/BB1/2013(H1N1), which shared high similarity with HuN EA-H1N1 virus; and blue indicates 2 human Eurasian avian-like influenza A(H1N1) isolates. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.
Main Article
Page created: October 18, 2016
Page updated: October 18, 2016
Page reviewed: October 18, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
