Volume 22, Number 11—November 2016
Dispatch
Increased Community-Associated Infections Caused by Panton-Valentine Leukocidin–Negative MRSA, Shanghai, 2005–2014
Figure
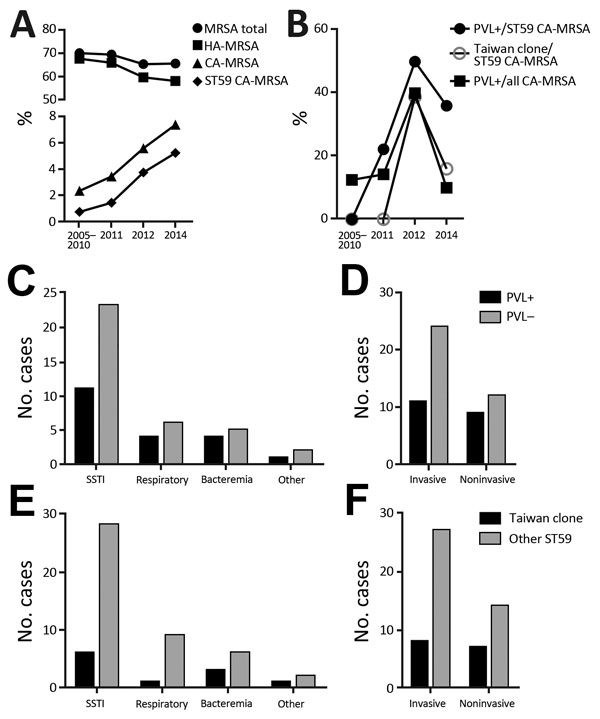
Figure. Epidemiology of MRSA in Shanghai, 2005–2014. Of infectious Staphylococcus aureus isolates obtained during 2005–2010, a random selection of 100 from each year were analyzed; of those obtained during 2001, 2012, and 2014, all isolates were analyzed. A) Percentages of MRSA (methicillin-resistant S. aureus) isolates among all obtained S. aureus isolates. B) Percentages of Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL)–positive clones among all or sequence type (ST) 59 community-associated (CA)–MRSA and of the Taiwan clone among ST59 CA-MRSA. C) Infection types from which ST59 CA-MRSA clones were obtained, differentiated by presence of PVL genes. D) Invasiveness of infections, differentiated by presence of PVL genes. E) Infection types from which ST59 CA-MRSA clones were obtained, differentiated by Taiwan clone versus other ST59 types. F) Invasiveness of infections, differentiated by Taiwan clone versus other ST59 types. HA, hospital acquired; SSTI, skin and soft tissue infection.
1These authors were co–principal investigators.
2These authors contributed equally to this article.