Volume 22, Number 12—December 2016
Dispatch
Genetically Different Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Viruses in West Africa, 2015
Figure
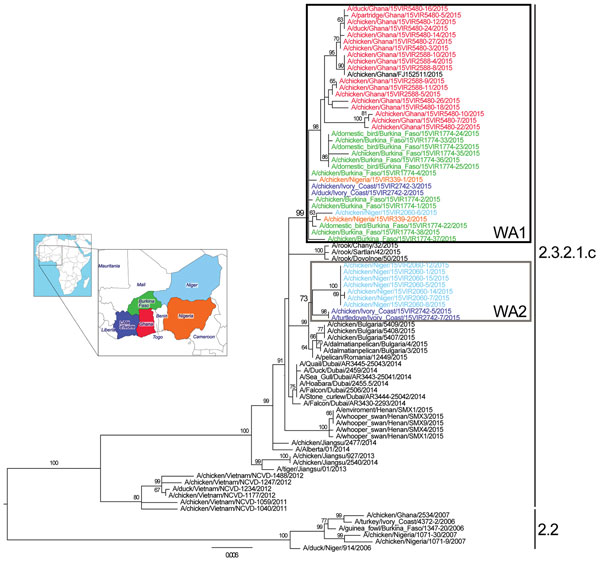
Figure. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of the hemagglutinin gene segment of highly pathogenic avian influenza (H5N1) viruses from West Africa. Strain colors indicate country of collection (inset). The 2 identified groups (WA1 and WA2) are indicated by boxes (black and gray, respectively). Clades are indicated at right; sequences from the 2006–2008 epidemic (clade 2.2) in West Africa were used as an outgroup. Numbers at the nodes represent bootstrap values >60%, obtained through a nonparametric bootstrap analysis that used 100 replicates. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
Page created: November 18, 2016
Page updated: November 18, 2016
Page reviewed: November 18, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.