Volume 22, Number 2—February 2016
Dispatch
Blastomyces gilchristii as Cause of Fatal Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Figure 1
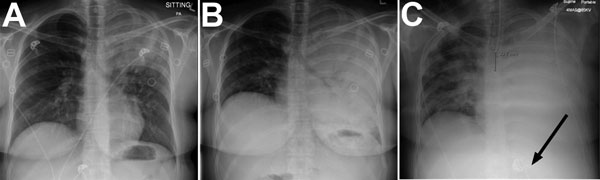
Figure 1. Chest radiograph at various stages of Blastomyces gilchristii infection in a 27-year-old woman, Ontario, Canada. A) Day 0: posterior–anterior (PA) chest radiograph at initial emergency department examination. Discrete confluent left upper lobe consolidation with air bronchograms are visible. B) Day 5, 15:10: PA chest radiograph demonstrating complete confluent opacification of the left hemithorax with extensive air bronchograms. C) Day 6, 23:30: PA chest radiograph postintubation with confluent left lung consolidation and new right patchy airspace opacification. Arrow indicates the correct placement of a nasogastric tube.
Page created: January 25, 2016
Page updated: January 25, 2016
Page reviewed: January 25, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.