Volume 22, Number 4—April 2016
Dispatch
Hypervirulent emm59 Clone in Invasive Group A Streptococcus Outbreak, Southwestern United States
Figure 2
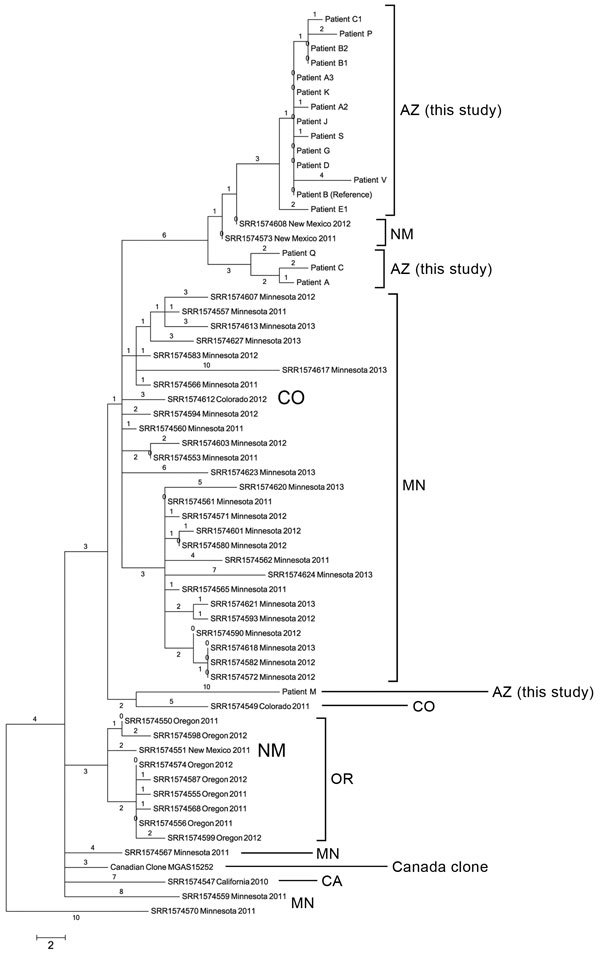
Figure 2. Phylogenetic single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) tree of emm59 isolates from Arizona during invasive group A Streptococcus outbreak in the southwestern United States, previously analyzed US emm59 isolates, and the Canadian clone. Maximum parsimony tree of all 177 SNP loci (44 parsimony informative SNPs) in emm59 isolates from Arizona (n = 18), Minnesota (n = 29), Oregon (n = 8), New Mexico (N = 3), Colorado (n = 2), and California (n = 1) and the Canadian clone reference isolate MGAS15252. Tree has regions of recombination removed and is rooted with Minnesota isolate SRR11574570. Consistency index = 1.0. Numbers above branches are SNP distances. Scale bar indicates SNPs.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: March 16, 2016
Page updated: March 16, 2016
Page reviewed: March 16, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.