Volume 22, Number 6—June 2016
Synopsis
Integration of Genomic and Other Epidemiologic Data to Investigate and Control a Cross-Institutional Outbreak of Streptococcus pyogenes
Figure 3
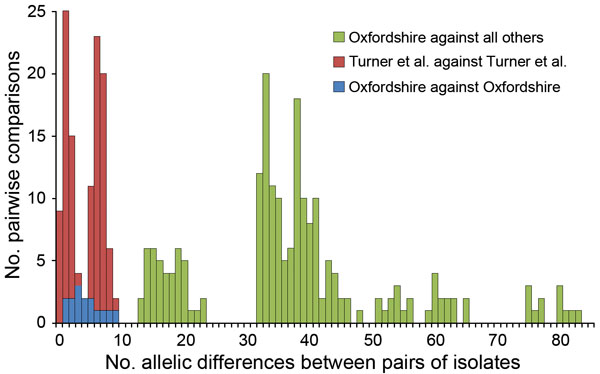
Figure 3. Pairwise allelic differences (across 1,514 genetic loci) among 6 isolates from a cross-institutional Streptococcus pyogenes outbreak in Oxfordshire, United Kingdom, and other isolates. Green indicates differences between each of the 6 Oxfordshire outbreak isolates and each of the other 33 isolates that occurred in other geographic areas in the United Kingdom around the time of the Oxfordshire outbreak or were reported by Turner et al. in 2013 (20). Red indicates differences between outbreak isolates from the cluster described by Turner et al. (20). Blue indicates differences between each isolate in the Oxfordshire outbreak compared with each of the other 5 isolates in the outbreak.
References
- Lamagni TL, Darenberg J, Luca-Harari B, Siljander T, Efstratiou A, Henriques-Normark B, Epidemiology of severe Streptococcus pyogenes disease in Europe. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:2359–67 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lepoutre A, Doloy A, Bidet P, Leblond A, Perrocheau A, Bingen E, Epidemiology of invasive Streptococcus pyogenes infections in France in 2007. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49:4094–100. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- O’Loughlin RE, Roberson A, Cieslak PR, Lynfield R, Gershman K, Craig A, The epidemiology of invasive group A streptococcal infection and potential vaccine implications: United States, 2000–2004. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:853–62. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Davies HD, McGeer A, Schwartz B, Green K, Cann D, Simor AE, Invasive group A streptococcal infections in Ontario, Canada. Ontario Group A Streptococcal Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:547–54 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lamagni TL, Neal S, Keshishian C, Powell D, Potz N, Pebody R, Predictors of death after severe Streptococcus pyogenes infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:1304–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Muller MP, Low DE, Green KA, Simor AE, Loeb M, Gregson D, Clinical and epidemiologic features of group a streptococcal pneumonia in Ontario, Canada. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:467–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rainbow J, Jewell B, Danila RN, Boxrud D, Beall B, Van Beneden C, Invasive group a streptococcal disease in nursing homes, Minnesota, 1995–2006. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:772–7 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thigpen MC, Richards CL Jr, Lynfield R, Barrett NL, Harrison LH, Arnold KE, Invasive group A streptococcal infection in older adults in long-term care facilities and the community, United States, 1998–2003. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1852–9 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zurawski CA, Bardsley M, Beall B, Elliott JA, Facklam R, Schwartz B, Invasive group A streptococcal disease in metropolitan Atlanta: a population-based assessment. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;27:150–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Daneman N, Green KA, Low DE, Simor AE, Willey B, Schwartz B, Surveillance for hospital outbreaks of invasive group A streptococcal infections in Ontario, Canada, 1992 to 2000. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147:234–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Steer JA, Lamagni T, Healy B, Morgan M, Dryden M, Rao B, Guidelines for prevention and control of group A streptococcal infection in acute healthcare and maternity settings in the UK. J Infect. 2012;64:1–18. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jordan HT, Richards CL Jr, Burton DC, Thigpen MC, Van Beneden CA. Group A streptococcal disease in long-term care facilities: descriptive epidemiology and potential control measures. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:742–52 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cummins A, Millership S, Lamagni T, Foster K. Control measures for invasive group A streptococci (iGAS) outbreaks in care homes. J Infect. 2012;64:156–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Invasive group A streptococcus in a skilled nursing facility—Pennsylvania, 2009–2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011;60:1445–9 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Greene CM, Van Beneden CA, Javadi M, Skoff TH, Beall B, Facklam R, Cluster of deaths from group A streptococcus in a long-term care facility—Georgia, 2001. Am J Infect Control. 2005;33:108–13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rahman M. Outbreak of Streptococcus pyogenes infections in a geriatric hospital and control by mass treatment. J Hosp Infect. 1981;2:63–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reid RI, Briggs RS, Seal DV, Pearson AD. Virulent Streptococcus pyogenes: outbreak and spread within a geriatric unit. J Infect. 1983;6:219–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McCarthy N. An epidemiological view of microbial genomic data. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:104–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Walker TM, Lalor MK, Broda A, Saldana Ortega L, Morgan M, Parker L, Assessment of Mycobacterium tuberculosis transmission in Oxfordshire, UK, 2007–12, with whole pathogen genome sequences: an observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2:285–92.
- Turner CE, Dryden M, Holden MT, Davies FJ, Lawrenson RA, Farzaneh L, Molecular analysis of an outbreak of lethal postpartum sepsis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:2089–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ben Zakour NL, Venturini C, Beatson SA, Walker MJ. Analysis of a Streptococcus pyogenes puerperal sepsis cluster by use of whole-genome sequencing. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:2224–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Health Protection Agency. Group A Streptococcus Working Group. Interim UK guidelines for management of close community contacts of invasive group A streptococcal disease. Commun Dis Public Health. 2004;7:354–61 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Johnson DR, Kaplan EL, Sramek J, Bicova R, Havlicek JHH, Havlickova H, Laboratory diagnosis of group A streptococcal infections. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1996 [cited 2014 Dec 20]. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/41879/1/9241544953_eng.pdf
- Bidet P, Lesteven E, Doit C, Liguori S, Mariani-Kurkdjian P, Bonacorsi S, Subtyping of emm1 group A streptococci causing invasive infections in France. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:4146–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:589–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010;20:1297–303. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zerbino DR, Birney E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008;18:821–9 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maiden MC, van Rensburg MJ, Bray JE, Earle SG, Ford SA, Jolley KA, MLST revisited: the gene-by-gene approach to bacterial genomics. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11:728–36. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stamatakis A. RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood–based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:2688–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jolley KA, Maiden MCJ. BIGSdb: scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11:595. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Banks DJ, Beres SB, Musser JM. The fundamental contribution of phages to GAS evolution, genome diversification and strain emergence. Trends Microbiol. 2002;10:515–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schwartz B, Ussery XT. Group A streptococcal outbreaks in nursing homes. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1992;13:742–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thigpen MC, Thomas DM, Gloss D, Park SY, Khan AJ, Fogelman VL, Nursing home outbreak of invasive group A streptococcal infections caused by 2 distinct strains. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2007;28:68–74 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stanley J, Desai M, Xerry J, Tanna A, Efstratiou A, George R. High-resolution genotyping elucidates the epidemiology of group A streptococcus outbreaks. J Infect Dis. 1996;174:500–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Athey TB, Teatero S, Li A, Marchand-Austin A, Beall BW, Fittipaldi N. Deriving group A Streptococcus typing information from short-read whole-genome sequencing data. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52:1871–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Davies MR, Holden MT, Coupland P, Chen JH, Venturini C, Barnett TC, Emergence of scarlet fever Streptococcus pyogenes emm12 clones in Hong Kong is associated with toxin acquisition and multidrug resistance. Nat Genet. 2015;47:84–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Smith A, Li A, Tolomeo O, Tyrrell GJ, Jamieson F, Fisman D. Mass antibiotic treatment for group A streptococcus outbreaks in two long-term care facilities. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:1260–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Arnold KE, Schweitzer JL, Wallace B, Salter M, Neeman R, Hlady WG, Tightly clustered outbreak of group A streptococcal disease at a long-term care facility. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2006;27:1377–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Milne LM, Lamagni T, Efstratiou A, Foley C, Gilman J, Lilley M, Streptococcus pyogenes cluster in a care home in England April to June 2010. Euro Surveill. 2011;16:20021 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
CrossRef reports the first author should be "High" not "Jordan" in reference 12 "Jordan, Richards, Burton, Thigpen, Van Beneden, 2007".
Reference has only first page number. Please provide the last page number if article is longer than one page. (in reference 30 "Jolley, Maiden, 2010").
CrossRef reports the year should be "2014" not "2015" in reference 37 "Davies, Holden, Coupland, Chen, Venturini, Barnett, et al., 2015".
Reference has only first page number. Please provide the last page number if article is longer than one page. (in reference 40 "Milne, Lamagni, Efstratiou, Foley, Gilman, Lilley, et al., 2011").