Volume 22, Number 7—July 2016
Letter
Pegivirus Infection in Domestic Pigs, Germany
Figure
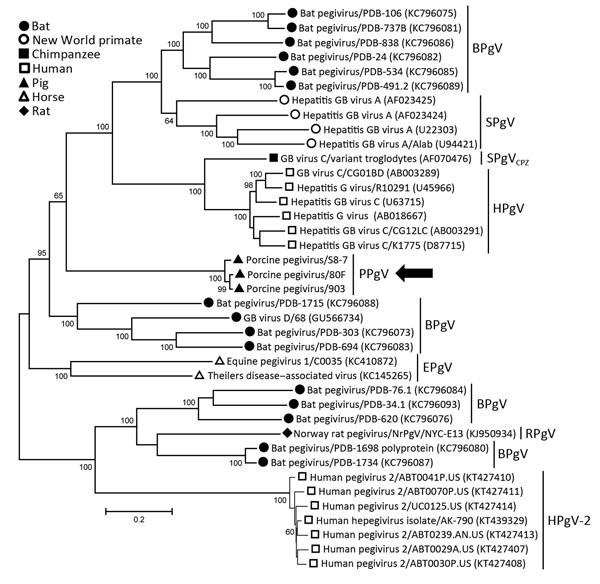
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of human and animal pegiviruses. We constructed a maximum-likelihood tree on the basis of the complete coding region and used the general time reversible model for modeling of substitutions. Bootstrap analysis was performed with 200 replicates. Numbers along branches are percentage bootstrap values. GenBank accession numbers are in parentheses. Arrow indicates viruses isolated in this study. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. BPgV, bat pegivirus, SPgV, simian pegivirus; SPgVCPZ, simian pegivirus (chimpanzee); HPgV, human pegivirus; PPgV, porcine pegivirus; EPgV, equine pegivirus; RPgV, rodent pegivirus. GB viruses have recently been reclassified as pegiviruses.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.