Volume 22, Number 8—August 2016
CME ACTIVITY - Research
Cutaneous Melioidosis Cluster Caused by Contaminated Wound Irrigation Fluid
Figure 2
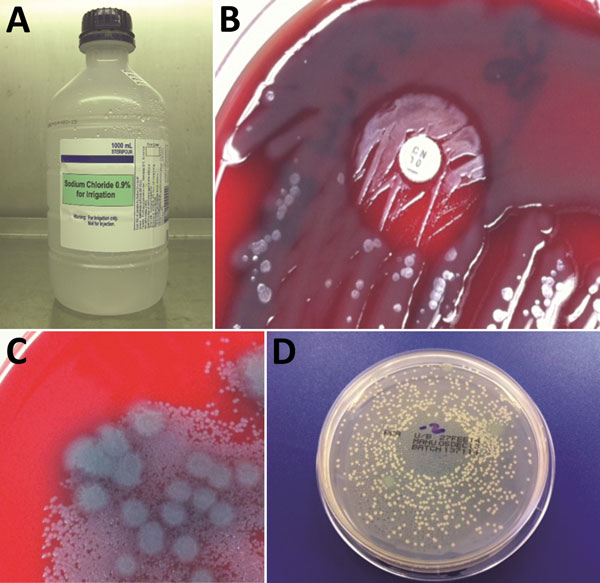
Figure 2. Bacterial culture results for 1,000-mL bottle of wound irrigation fluid in laboratory investigation of a 2012–2013 cutaneous melioidosis cluster in the temperate southern region of Western Australia. A) Wound irrigation fluid in original bottle. B) Direct primary culture of wound irrigation fluid on blood agar plate, showing growth inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and revealing Burkholderia pseudomallei around gentamicin disk. C) Filtrate of wound irrigation fluid from same bottle showing higher count of B. pseudomallei colonies than P. aeruginosa. D) Dilution of wound irrigation fluid (1:100), dispensed by spiral plating device, showing B. pseudomallei colonies and relatively sparse P. aeruginosa colonies.
Page created: July 08, 2016
Page updated: July 08, 2016
Page reviewed: July 08, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.