Volume 23, Number 10—October 2017
Research Letter
Mycobacterium orygis Lymphadenitis in New York, USA
Figure
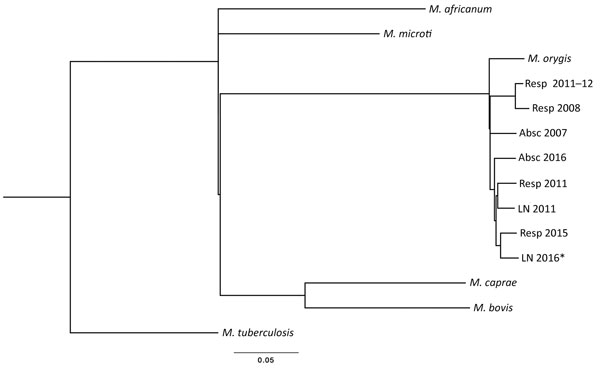
Figure. Maximum-likelihood single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) tree of 8 Mycobacterium orygis and 1 M. caprae isolates obtained from patients in New York, USA. Alignment of 5,242 total SNP positions was calculated by using PhyML version 20111216 (http://www.atgc-montpellier.fr/phyml/) general time reversible plus gamma model under 8 categories with best of nearest-neighbor interchange, subtree pruning, and regrafting with 5 random starting trees. Included in the tree are M. tuberculosis H37Rv (GenBank accession no. NC_000962), M. orygis (accession no. APKD01000001.1), M. bovis (accession no. NC_002945.3), M. africanum (accession no. NC_015758.1), and M. microti (ATCC 35782) reference sequences. SNP analysis of the isolate from the patient described in this study (LN 2016) with 7 other M. orygis strains identified at the New York State Department of Health showed differences ranging from 170 (closest) to 323 (farthest) SNPs. By comparison, the closest non–M. orygis M. tuberculosis complex species is M. microti (1,880 SNPs). All M. orygis strains are grouped with 100% bootstrap support. Scale bar indicates average number of substitutions per site. Specimen sources: Resp, respiratory; Absc, abcess; LN, lymph node (BioProject ID PRJNA389109 containing BioSample accessions SAMN07190143–50).