Volume 23, Number 11—November 2017
Research
Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis among Children, China, 2006–2015
Figure 1
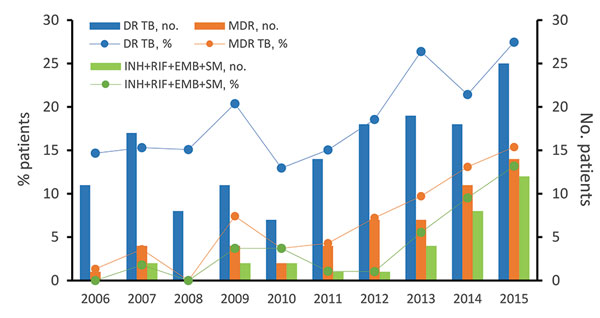
Figure 1. Trends for DR TB and MDR TB among children with primary cases of TB, Shandong Province, China, 2006–2015. The χ2 and linear regression results are shown in Table 3. DR TB, drug-resistant TB; EMB, ethambutol; INH, isoniazid; MDR, multidrug-resistant; RIF, rifampin; SM, streptomycin; TB, tuberculosis.
Page created: October 16, 2017
Page updated: October 16, 2017
Page reviewed: October 16, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.