Volume 23, Number 11—November 2017
Dispatch
High-Level Fosfomycin Resistance in Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium
Figure
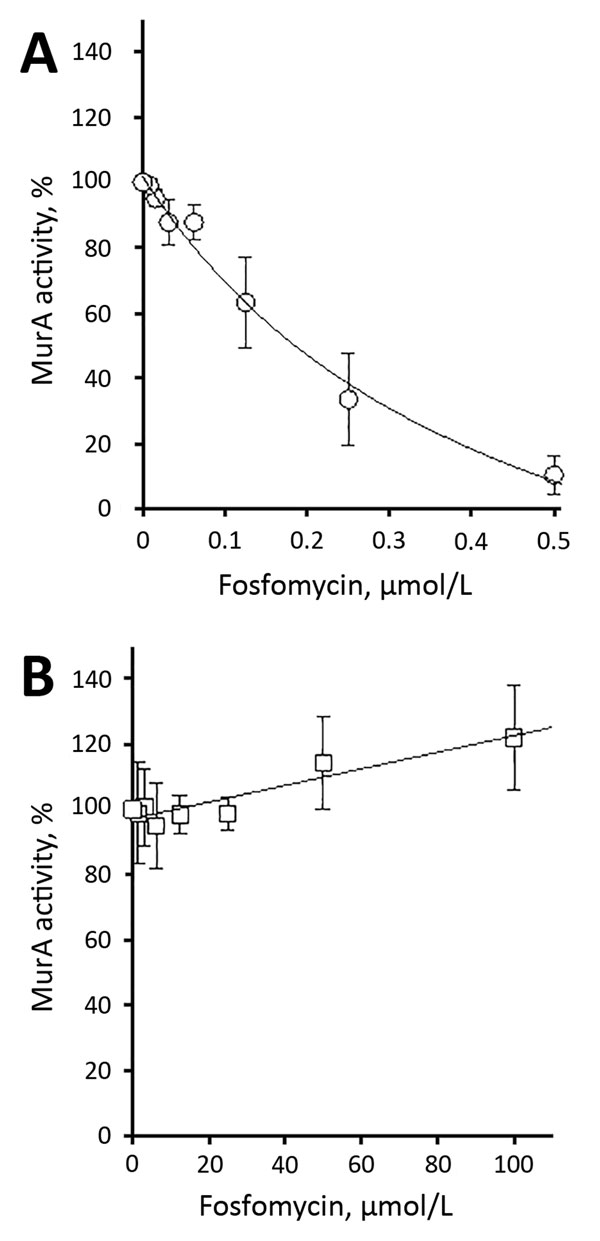
Figure. Inhibition of recombinant purified vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium wild-type (A) and C119D (B) MurA by fosfomycin. The 50% inhibitory concentration was 176.8 ± 38.3 nmol/L for wild-type MurA and >100 μmol/L for C119D MurA. Error bars indicate mean ± SD of >3 independent experiments. MurA, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase.
Page created: October 17, 2017
Page updated: October 17, 2017
Page reviewed: October 17, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.