Volume 23, Number 12—December 2017
Research Letter
Moku Virus in Invasive Asian Hornets, Belgium, 2016
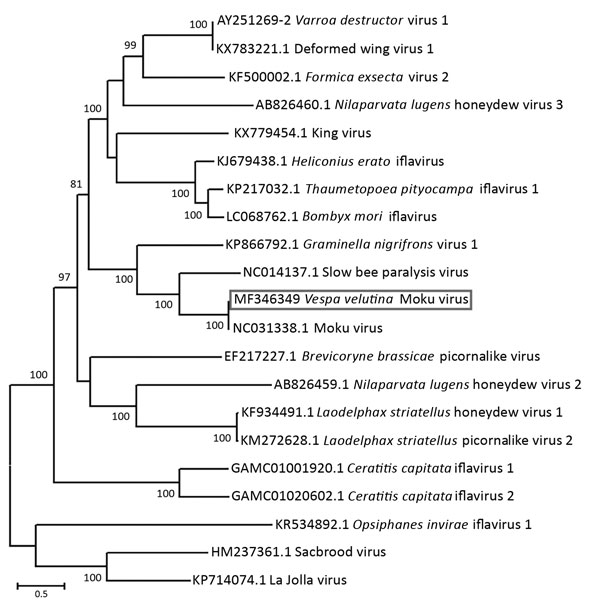
. Evolutionary relationships of Moku virus generated from a pool of 5 female and 5 male Asian hornets () collected in Belgium in 2016 (box) compared with representative members of the genus , based on the maximum-likelihood phylogeny of the polyprotein sequences. The phylogenetic analysis was performed using MEGA6 () and the LG substitution model, as determined by a model selection analysis. Bootstrap percentages >70% (from 500 resamplings) are indicated at each node. GenBank accession numbers are indicated for each species. Scale bar indicates amino acid substitutions per site.
Page created: November 16, 2017
Page updated: November 16, 2017
Page reviewed: November 16, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.