Volume 23, Number 4—April 2017
Synopsis
Implementation and Initial Analysis of a Laboratory-Based Weekly Biosurveillance System, Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur, France
Figure 2
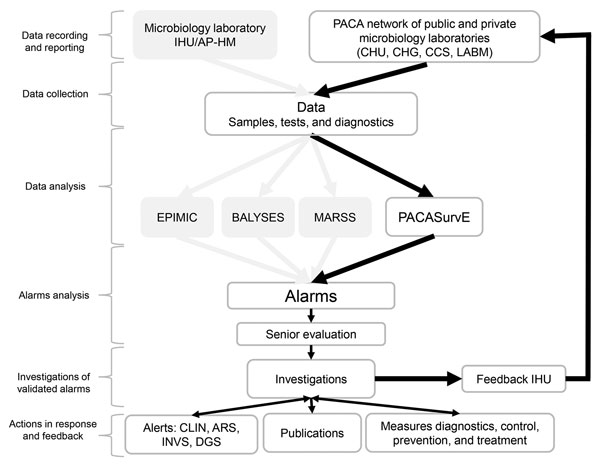
Figure 2. Flow diagram of all epidemiologic surveillance systems implemented by the Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditérannée Infection, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Marseille, France. ARS, Agence Régionale de Santé (Regional Health Agency); BALYSES, Bacterial Real-Time Laboratory-Based Surveillance System; CDS, Centre de Santé (Health Center); CHG, Centre Hospitalier Général (General Hospital Center); CHU, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire (Central University Hospital); CLIN, Comité de Lutte contre les Infections Nosocomiales (Committee for the Fight Against Nosocomial Infections); DGS, Direction Générale de la Santé (Directorate General for Health); EPIMIC, Epidemiologic Surveillance and Alert Based on Microbiological Data; IHU/AP-HM, Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire/Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Marseille; INVS, Institut Nationale de Veille Sanitaire (National Institute for Public Health Surveillance); LABM, Laboratoire de Biologie Médicale (Medical Laboratory); MARSS, Marseille Antibiotic Resistance Surveillance System; PACASurvE, Provence Alpes Côte d’Azur Surveillance Epidemiologic System. Diagram is based on the workflow described by Abat et Al. 2013 (10).
References
- Raoult D. The causes underlying the emergence of disease agents [in French]. Annales des Mines—Responsabilité et Environnement. 2008;3:21–4. https://dx.doi.org/10.3917/re.051.0021
- GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385:117–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Declich S, Carter AO. Public health surveillance: historical origins, methods and evaluation. Bull World Health Organ. 1994;72:285–304.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- M’ikanatha N, de Valk H, Lynfield R, Van Benden C. Infectious disease surveillance: a cornerstone for prevention and control. In: M’ikanatha N, de Valk H, Lynfield R, Van Benden C, editors. Introduction to infectious disease surveillance. 2nd ed. Oxford: John Wiley & Sons; 2013. p. 1–20.
- Morens DM, Folkers GK, Fauci AS. The challenge of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Nature. 2004;430:242–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- De Cos H. Treatise on the airs, waters, and places. In: É Littré. Complete works of Hippocrates [in French]. Vol. 2. Paris: J.B. Baillière; 1840. p. 1–93.
- Abat C, Chaudet H, Rolain J-M, Colson P, Raoult D. Traditional and syndromic surveillance of infectious diseases and pathogens. Int J Infect Dis. 2016;48:22–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Buckeridge D. Detection of outbreaks using laboratory data: an epidemiological perspective [cited 2016 Dec 22]. https://www.inspq.qc.ca/sites/default/files/jasp/archives/2006/jasp2006-laboratoire-lbuckeridge1.pdf
- Colson P, Rolain J-M, Abat C, Charrel R, Fournier P-E, Raoult D. EPIMIC: a simple homemade computer program for real-time epidemiological surveillance and alert based on microbiological data. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0144178. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Abat C, Chaudet H, Colson P, Rolain J-M, Raoult D. Real-time microbiology laboratory surveillance system to detect abnormal events and emerging infections, Marseille, France. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:1302–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Seng P, Abat C, Rolain JM, Colson P, Lagier J-C, Gouriet F, et al. Identification of rare pathogenic bacteria in a clinical microbiology laboratory: impact of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:2182–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Plouin-Gaudon I, Vanhems P, Allard R, Sahajian F, Fabry J. [Surveillance of laboratory based infections by biological and medical analyses: review of the literature] [in French]. Sante Publique. 2000;12:149–59.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Enki DG, Noufaily A, Garthwaite PH, Andrews NJ, Charlett A, Lane C, et al. Automated biosurveillance data from England and Wales, 1991-2011. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:35–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Walckiers D, Vandepitte J, Stroobant A, Cornelis R, Van Casteren VD, Walckiers JV. A new method of surveillance of infectious diseases in Belgium: the “Vigie” network of microbiology laboratories [in French]. Med Mal Infect. 1986;16:147–50. DOIGoogle Scholar
- French National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies. Legal population in force as of January 1, 2014: census of population [in French] [cited 2016 Apr 1]. https://www.insee.fr/fr/statistiques/fichier/2119747/dep91.pdf
- Hulth A, Andrews N, Ethelberg S, Dreesman J, Faensen D, van Pelt W, et al. Practical usage of computer-supported outbreak detection in five European countries. Euro Surveill. 2010;15:19658.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing [cited 2016 Dec 22]. http://www.R-project.org
- Hutwagner L, Thompson W, Seeman GM, Treadwell T. The bioterrorism preparedness and response Early Aberration Reporting System (EARS). J Urban Health. 2003;80(Suppl 1):i89–96.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang X, Zeng D, Seale H, Li S, Cheng H, Luan R, et al. Comparing early outbreak detection algorithms based on their optimized parameter values. J Biomed Inform. 2010;43:97–103. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Abat C, Huart M, Garcia V, Dubourg G, Raoult D. Enterococcus faecalis urinary-tract infections: do they have a zoonotic origin? J Infect. 2016;2016:305–13. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2016.07.012PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lagier J-C, Dubourg G, Cassir N, Fournier P-E, Colson P, Richet H, et al. Clostridium difficile 027 emerging outbreak in Marseille, France. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2013;34:1339–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Huart M, Abat C, Jimeno MT, Deparis X, Raoult D, Fournier P-E. Compared lethality rates of Clostridium difficile infections at the local, regional and national levels in France. New Microbes New Infect. 2016;14:6–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lagier J-C, Delord M, Million M, Parola P, Stein A, Brouqui P, et al. Dramatic reduction in Clostridium difficile ribotype 027-associated mortality with early fecal transplantation by the nasogastric route: a preliminary report. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;34:1597–601 . https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10096-015-2394-xPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Walckiers D, Stroobant A, Yourassowsky E, Lion J, Cornelis R. A sentinel network of microbiological laboratories as a tool for surveillance of infectious diseases in Belgium. Epidemiol Infect. 1991;106:297–303. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kalish BT, Gaydos CA, Hsieh Y-H, Christensen BE, Carroll KC, Cannons A, et al. National survey of Laboratory Response Network sentinel laboratory preparedness. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2009;3(Suppl):S17–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Walckiers D, Van Ros G, Stroobant A. [Monitoring of malaria in Belgium through a network of microbiology laboratories] [in French]. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1986;66:15–21.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Silva JC, Shah SC, Rumoro DP, Bayram JD, Hallock MM, Gibbs GS, et al. Comparing the accuracy of syndrome surveillance systems in detecting influenza-like illness: GUARDIAN vs. RODS vs. electronic medical record reports. Artif Intell Med. 2013;59:169–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Farrington CP, Andrews NJ, Beale AD, Catchpole MA. A statistical algorithm for the early detection of outbreaks of infectious disease. J R Stat Soc Ser A Stat Soc. 1996;159:547–63. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Buckeridge DL, Burkom H, Campbell M, Hogan WR, Moore AW. Algorithms for rapid outbreak detection: a research synthesis. J Biomed Inform. 2005;38:99–113. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fricker RD Jr, Hegler BL, Dunfee DA. Comparing syndromic surveillance detection methods: EARS’ versus a CUSUM-based methodology. Stat Med. 2008;27:3407–29. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar