Volume 23, Number 4—April 2017
CME ACTIVITY - Synopsis
Transmission of Hepatitis A Virus through Combined Liver–Small Intestine–Pancreas Transplantation
Figure 1
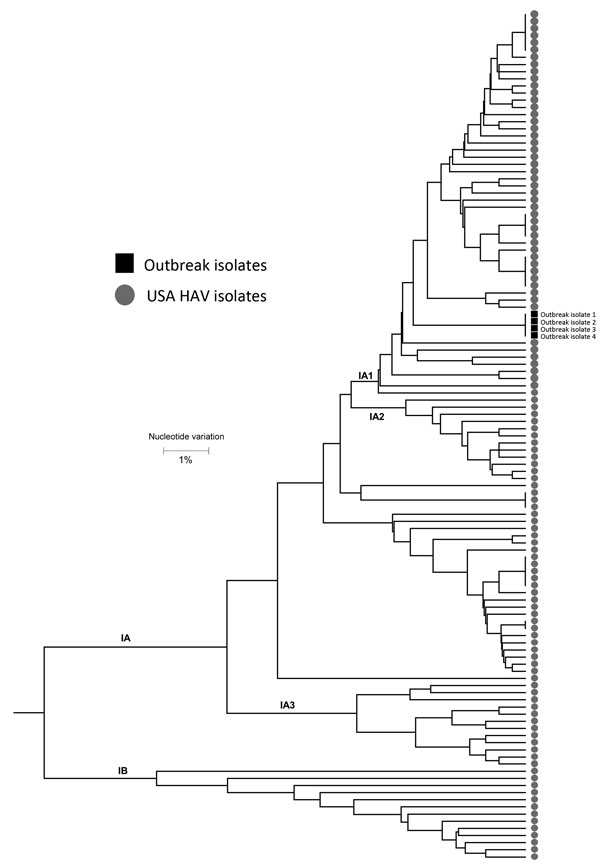
Figure 1. Polygenetic analysis of HAV isolates within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s US HAV database. The genomic regions are the 315-bp long HAV VP1/P2B (viral protein 1/amino terminus of 2B). Black squares indicate isolates from the outbreak of HAV transmitted through a combined liver–small intestine–pancreas transplantation, Texas, USA, 2014–2015. Scale bar indicates nucleotide variation. HAV, hepatitis A virus.
Page created: March 13, 2017
Page updated: March 13, 2017
Page reviewed: March 13, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.