Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N8) Virus in Wild Migratory Birds, Qinghai Lake, China
Mingxin Li
1, Haizhou Liu
1, Yuhai Bi
1, Jianqing Sun
1, Gary Wong, Di Liu, Laixing Li, Juxiang Liu, Quanjiao Chen, Hanzhong Wang, Yubang He, Weifeng Shi, George F. Gao, and Jianjun Chen

Author affiliations: CAS Key Laboratory of Special Pathogens and Biosafety, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hubei, China (M. Li, H. Liu, J. Liu, Q. Chen, H. Wang, J. Chen); Center for Influenza Research and Early-warning (CASCIRE), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing (Y. Bi, G. Wong, D. Liu, Q. Chen, G.F. Gao, J. Chen); Key Laboratory of Pathogenic Microbiology and Immunology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China (Y. Bi, G. Wong, D. Liu, G.F. Gao); Shenzhen Third People’s Hospital, Shenzhen, China (Y. Bi, G.F. Gao); Qinghai Lake National Nature Reserve, Qinghai, China (J. Sun, Y. He); Northwest Institute of Plateau Biology of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xining, China (L. Li); Institute of Pathogen Biology, Taishan Medical College, Shandong, China (W. Shi)
Main Article
Figure 1
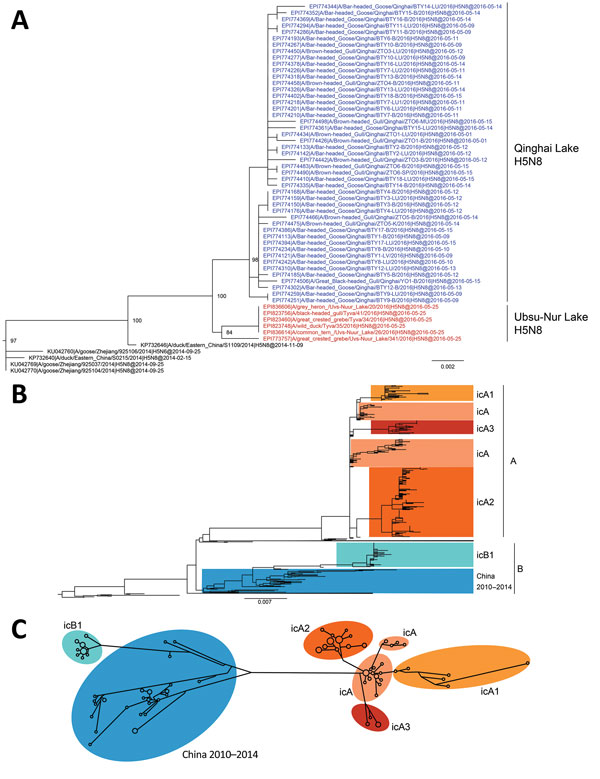
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analyses of 594 hemagglutinin (HA) sequences (1,704 nt) from clade 2.3.4.4 H5 influenza viruses. A) HA-coding sequence subtree from maximum-likelihood phylogenetic analysis of the clade 2.3.4.4 H5 viruses. Colored nodes: blue, Qinghai Lake H5N8 strains (this study); red, Ubsu-Nur Lake H5N8 strains. B) Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of the clade 2.3.4.4 HA-coding sequences, rooted with A/Goose/Guangdong/1/96(H5N1). Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site. C) Median-joining phylogenetic network of the HA-coding gene sequences, including the most parsimonious trees linking the sequences. To simplify the network, nodes with only one sequence are not shown. Network branch lengths are proportional to the numbers of mutations. icA, intercontinental group A; icA1, intercontinental subgroup A1; icA2, intercontinental subgroup A2; icA3, intercontinental subgroup A3; icB1, intracontinental subgroup B1.
Main Article
Page created: March 17, 2017
Page updated: March 17, 2017
Page reviewed: March 17, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
