Volume 23, Number 5—May 2017
Research
Use of Blood Donor Screening Data to Estimate Zika Virus Incidence, Puerto Rico, April–August 2016
Figure 1
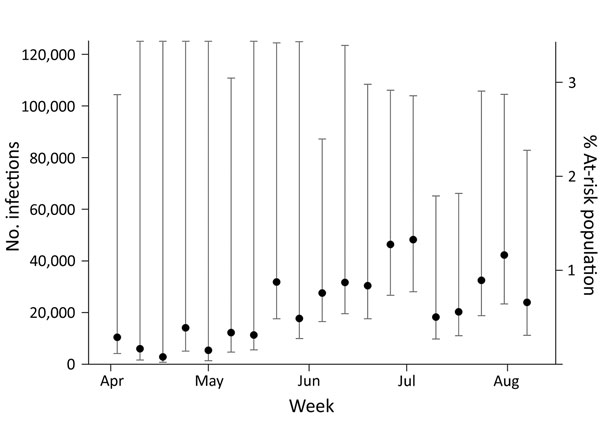
Figure 1. Individual weekly estimates of the number and percentage of at-risk population with incident Zika virus infections computed with cobas Zika (Roche Molecular Systems, Inc., Pleasanton, CA, USA) individual nucleic acid testing results from Banco de Sangre de Servicios Mutuos and Banco de Sangre del Centro Médico de la Administración de Servicios Médicos, Puerto Rico, April 3–August 12, 2016. These estimates assume a mean viremia duration of 9.9 days (SD ± 3.9). To retain readability of the point estimates, some of the confidence interval line segments extend beyond the vertical boundary. Data for August 1–August 12, 2016 available only for Banco de Sangre de Servicios Mutuos. Error bars indicate 95% CIs.
Page created: April 17, 2017
Page updated: April 17, 2017
Page reviewed: April 17, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.