Volume 23, Number 6—June 2017
Dispatch
Brucella neotomae Infection in Humans, Costa Rica
Figure 2
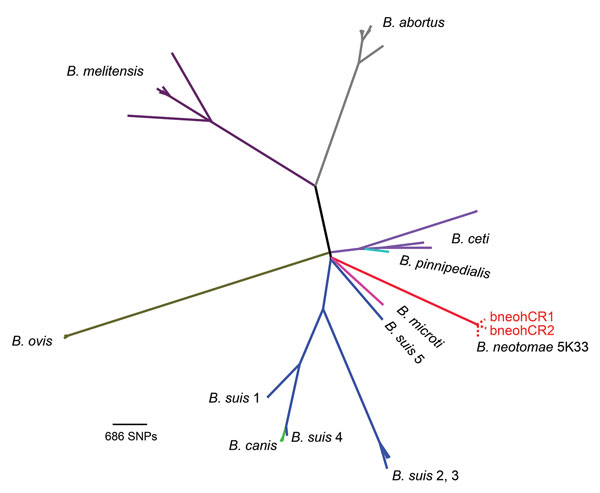
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree based on 34,307 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) found among 51 Brucella genome sequences. The clinical isolates bneohCR1 and bneohCR2 cluster with B. neotomae 5K33 and differ by 164 SNPs. A different color is used to represent each Brucella species. Dotted red lines denote the 3 B. neotomae isolates, which overlap at the tip of the branch because of the high identity among them.
1Current affiliation: University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK
Page created: July 11, 2017
Page updated: July 11, 2017
Page reviewed: July 11, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.