Volume 23, Number 9—September 2017
Research
Processes Underlying Rabies Virus Incursions across US–Canada Border as Revealed by Whole-Genome Phylogeography
Figure 3
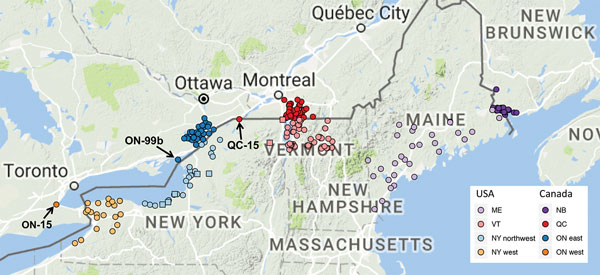
Figure 3. Locations of sequenced samples from Canada outbreaks of raccoon-specific variant of rabies virus infection in western Ontario (n = 1), eastern Ontario (n = 56), Quebec (n = 51), and New Brunswick (n = 32); and from the United States within 75 km of the border in western New York (n = 23), northwestern New York (n = 29, including 5 samples into clade I, indicated by squares), and Vermont (n = 64, including 2 samples from New York that grouped within this clade, indicated by squares); and from throughout Maine (n = 33). Map generated by using ggmap package (20). NB, New Brunswick; ON, Ontario; QC, Quebec.
References
- Wandeler AI, Rosatte RC, Williams D, Lee TK, Gensheimer KF, Montero JT, et al.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update: raccoon rabies epizootic—United States and Canada, 1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2000;49:31–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sterner RT, Meltzer MI, Shwiff SA, Slate D. Tactics and economics of wildlife oral rabies vaccination, Canada and the United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:1176–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Moore DA. Spatial diffusion of raccoon rabies in Pennsylvania, USA. Prev Vet Med. 1999;40:19–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wilson ML, Bretsky PM, Cooper GH Jr, Egbertson SH, Van Kruiningen HJ, Cartter ML. Emergence of raccoon rabies in Connecticut, 1991-1994: spatial and temporal characteristics of animal infection and human contact. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;57:457–63. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lucey BT, Russell CA, Smith D, Wilson ML, Long A, Waller LA, et al. Spatiotemporal analysis of epizootic raccoon rabies propagation in Connecticut, 1991-1995. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2002;2:77–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Biek R, Henderson JC, Waller LA, Rupprecht CE, Real LA. A high-resolution genetic signature of demographic and spatial expansion in epizootic rabies virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:7993–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stevenson B, Goltz J, Massé A. Preparing for and responding to recent incursions of raccoon rabies variant into Canada. Can Commun Dis Rep. 2016;42:125–9 [cited 2017 Jun 22]. http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/publicat/ccdr-rmtc/16vol42/dr-rm42-6/assets/pdf/16vol42_6-ar-03-eng.pdf
- Rosatte RC, Donovan D, Allan M, Bruce L, Buchanan T, Sobey K, et al. The control of raccoon rabies in Ontario Canada: proactive and reactive tactics, 1994-2007. J Wildl Dis. 2009;45:772–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rosatte R, MacDonald E, Sobey K, Donovan D, Bruce L, Allan M, et al. The elimination of raccoon rabies from Wolfe Island, Ontario: animal density and movements. J Wildl Dis. 2007;43:242–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shwiff S, Aenishaenslin C, Ludwig A, Berthiaume P, Bigras-Poulin M, Kirkpatrick K, et al. Bioeconomic modelling of raccoon rabies spread management impacts in Quebec, Canada. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2013;60:330–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nadin-Davis SA, Colville A, Trewby H, Biek R, Real L. Application of high-throughput sequencing to whole rabies viral genome characterisation and its use for phylogenetic re-evaluation of a raccoon strain incursion into the province of Ontario. Virus Res. 2017;232:123–33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Drummond AJ, Ho SYW, Phillips MJ, Rambaut A. Relaxed phylogenetics and dating with confidence. PLoS Biol. 2006;4:e88. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lemey P, Rambaut A, Drummond AJ, Suchard MA. Bayesian phylogeography finds its roots. PLOS Comput Biol. 2009;5:e1000520. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol Biol Evol. 2012;29:1969–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ayres DL, Darling A, Zwickl DJ, Beerli P, Holder MT, Lewis PO, et al. BEAGLE: an application programming interface and high-performance computing library for statistical phylogenetics. Syst Biol. 2012;61:170–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bielejec F, Rambaut A, Suchard MA, Lemey P. SPREAD: spatial phylogenetic reconstruction of evolutionary dynamics. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:2910–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Minin VN, Suchard MA. Fast, accurate and simulation-free stochastic mapping. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2008;363:3985–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Szanto AG, Nadin-Davis SA, Rosatte RC, White BN. Genetic tracking of the raccoon variant of rabies virus in eastern North America. Epidemics. 2011;3:76–87. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nadin-Davis SA, Muldoon F, Wandeler AI. A molecular epidemiological analysis of the incursion of the raccoon strain of rabies virus into Canada. Epidemiol Infect. 2006;134:534–47. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kahle D, Wickham H. ggmap: spatial visualization with ggplot2. The R Journal. 2013;5:144–61 [cited 2017 June 22]. http://journal.r-project.org/archive/2013-1/kahle-wickham.pdf
- MacInnes C. Raccoon rabies in New Brunswick. Rabies report. Peterborough (Ontario, Canada); Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources; 2000; vol. 11. p. 10.
- Henderson JC, Biek R, Hanlon CA, O’Dee S, Real LA. Rabies virus in raccoons, Ohio, 2004. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:650–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cullingham CI, Pond BA, Kyle CJ, Rees EE, Rosatte RC, White BN. Combining direct and indirect genetic methods to estimate dispersal for informing wildlife disease management decisions. Mol Ecol. 2008;17:4874–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dharmarajan G, Beasley JC, Fike JA, Rhodes OE. Population genetic structure of raccoons (Procyon lotor) inhabiting a highly fragmented landscape. Can J Zool. 2009;87:814–24. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Rosatte R, Ryckman M, Ing K, Proceviat S, Allan M, Bruce L, et al. Density, movements, and survival of raccoons in Ontario, Canada: implications for disease spread and management. J Mammal. 2010;91:122–35. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Rosatte R, Sobey K, Donovan D, Bruce L, Allan M, Silver A, et al. Behavior, movements, and demographics of rabid raccoons in Ontario, Canada: management implications. J Wildl Dis. 2006;42:589–605. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rosatte R, Sobey K, Donovan D, Allan M, Bruce L, Buchanan T, et al. Raccoon density and movements after population reduction to control rabies. J Wildl Manage. 2007;71:2373–8. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Rosatte R, Donovan D, Allan M, Howes LA, Silver A, Bennett K, et al. Emergency response to raccoon rabies introduction into Ontario. J Wildl Dis. 2001;37:265–79. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nettles VF, Shaddock JH, Sikes RK, Reyes CR. Rabies in translocated raccoons. Am J Public Health. 1979;69:601–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: August 14, 2017
Page updated: August 14, 2017
Page reviewed: August 14, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.