Volume 24, Number 1—January 2018
Research
Geogenomic Segregation and Temporal Trends of Human Pathogenic Escherichia coli O157:H7, Washington, USA, 2005–20141
Figure 2
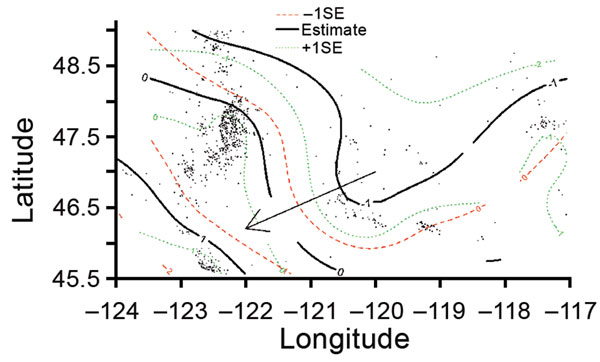
Figure 2. Risk surface of Escherichia coli O157:H7 lineage IIb relative to lineage Ib using a multinomial generalized additive model and a bivariate thin plate smooth function for longitude and latitude for culture-confirmed human cases reported in Washington, USA, 2005–2014. The black contour lines show the mean effect estimate for lineage IIb relative to Ib as latitude and longitude change. The 0-marked black line indicates no effect. The 1-marked black line indicates greater proportional incidence of lineage IIb toward the southwest corner of the area as compared to lineage Ib (p<0.001). The arrow indicates the general direction of the trend from higher Ib risk to higher IIb risk. Dashed red lines show the effect estimate 1 standard error (SE) below (to the south and west) the mean estimate. Dotted green lines show the effect estimate 1 standard error above (to the north and east) the mean estimate.
1Preliminary results from this study were presented at the International Meeting on Emerging Diseases and Surveillance (IMED), November 4–7, 2016, Vienna, Austria.