Volume 24, Number 11—November 2018
Dispatch
Fatal Case of Diphtheria and Risk for Reemergence, Singapore
Figure 1
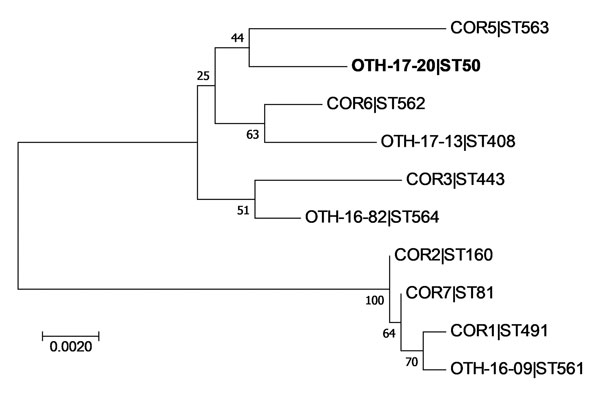
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of Corynebacterium diphtheriae isolate from a 23-year-old man who died from diphtheria (OTH-17-20; bold) and 9 other isolates collected from hospitals in Singapore during 2013–2017. The tree was constructed by using 7 concatenated housekeeping gene sequences corresponding to the C. diphtheriae multilocus sequence typing scheme (https://pubmlst.org/cdiphtheriae/). Sequences were extracted from whole-genome sequences of each isolate. Concatenated sequences were aligned by using ClustalW (http://www.clustal.org/). Phylogeny was inferred by using the maximum-likelihood method, neighbor-joining algorithm based on the Jukes-Cantor model, and MEGA7 software (10). There were 2,544 positions in the final dataset. Numbers next to branches show bootstrap values calculated by using 1,000 reiterations. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. ST, sequence type.
References
- Tiwari TS, Wharton M. Diphtheria toxoid. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit P, editors. Plotkin’s vaccines. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2017. p. 261–75.
- World Health Organization. Immunization, vaccines and biologicals: data, statistics and graphs [cited 2018 Apr 9]. http://www.who.int/immunization/monitoring_surveillance/data/en/
- Clarke KE. Review of the epidemiology of diphtheria, 2000–2016 [cited 2018 Apr 9]. http://www.who.int/immunization/sage/meetings/2017/april/1_Final_report_Clarke_april3.pdf?ua=1
- Berger A, Meinel DM, Schaffer A, Ziegler R, Pitteroff J, Konrad R, et al. A case of pharyngeal diphtheria in Germany, June 2015. Infection. 2016;44:673–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rasmussen I, Wallace S, Mengshoel AT, Høiby EA, Brandtzæg P. Diphtheria outbreak in Norway: lessons learned. Scand J Infect Dis. 2011;43:986–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. A case of diphtheria in Spain, June 15, 2015 [cited 2018 Aug 15]. https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/media/en/publications/Publications/diphtheria-spain-rapid-risk-assessment-june-2015.pdf
- Perkins S, Cordery R, Nixon G, Abrahams A, Andrews J, White J, et al. Investigations and control measures following a non-travel-associated case of toxigenic Cornyebacterium diphtheriae, London, United Kingdom, December 2009-January 2010. Euro Surveill. 2010;15:19544.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ministry of Health Singapore. Communicable diseases surveillance in Singapore 2016 [cited 2018 Apr 9]. https://www.moh.gov.sg/content/dam/moh_web/Publications/Reports/2017/Full%20Version.pdf
- Nakao H, Pruckler JM, Mazurova IK, Narvskaia OV, Glushkevich T, Marijevski VF, et al. Heterogeneity of diphtheria toxin gene, tox, and its regulatory element, dtxR, in Corynebacterium diphtheriae strains causing epidemic diphtheria in Russia and Ukraine. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:1711–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33:1870–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Diphtheria Guidelines Working Group, Public Health England. Public health control and management of diphtheria (in England and Wales), 2015 guidelines [cited 2018 Aug 15]. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/diphtheria-public-health-control-and-management-in-england-and-wales
- Lumio J, Suomalainen P, Olander RM, Saxén H, Salo E. Fatal case of diphtheria in an unvaccinated infant in Finland. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22:844–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Farizo KM, Strebel PM, Chen RT, Kimbler A, Cleary TJ, Cochi SL. Fatal respiratory disease due to Corynebacterium diphtheriae: case report and review of guidelines for management, investigation, and control. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;16:59–68. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bowler IC, Mandal BK, Schlecht B, Riordan T. Diphtheria—the continuing hazard. Arch Dis Child. 1988;63:194–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Simmons LE, Abbott JD, Macaulay ME, Jones AE, Ironside AG, Mandal BK, et al. Diphtheria carriers in Manchester: simultaneous infection with toxigenic and non-toxigenic mitis strains. Lancet. 1980;1:304–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar