Volume 24, Number 12—December 2018
Research
CTX-M-65 Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase–Producing Salmonella enterica Serotype Infantis, United States1
Figure 2
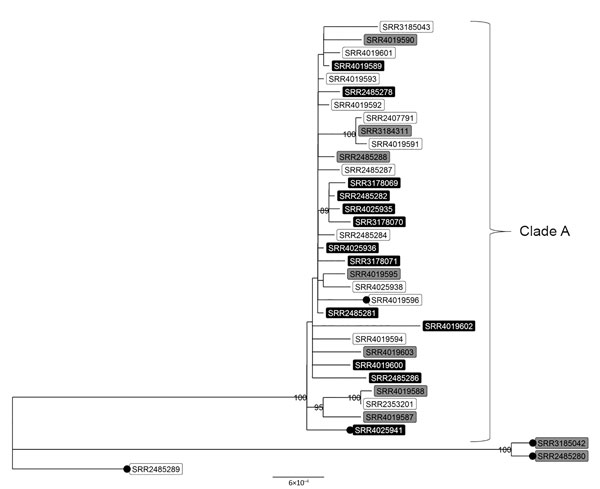
Figure 2. High-quality single-nucleotide polymorphism–based phylogenetic tree of clinical and retail meat isolates of Salmonella enterica serotype Infantis with pulsed-field gel electrophoresis pattern JFXX01.0787 collected in the United States and submitted to the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System for whole-genome sequencing. Tree tips are labeled with National Center for Biotechnology Information accession numbers (sequence read archive run identification numbers); shading indicates patients’ international travel history for clinical isolates (black, recent international travel; gray, no recent international travel; white, travel data missing). Black circles indicate isolates that are missing the blaCTX-M-65 gene. Isolates in top clade differed by 2–47 high-quality single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Numbers displayed on nodes are bootstrap support values, an indication of the reliability of the tree. Only bootstrap values >80 are displayed. More information on patient and isolate characteristics are provided in Tables 1 and 2. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
1Preliminary results from this analysis were presented at the International Salmonella and Salmonellosis Symposium, June 6–8, 2016, St. Malo, France, and at the International Association for Food Protection Annual Meeting, July 9–12, 2017, Tampa, Florida, USA.