Use of Pristinamycin for Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma genitalium Infection
Tim R.H. Read

, Jørgen S. Jensen, Christopher K. Fairley, Mieken Grant, Jennifer A. Danielewski, Jenny Su, Gerald L. Murray, Eric P.F. Chow, Karen Worthington, Suzanne M. Garland, Sepehr N. Tabrizi, and Catriona S. Bradshaw
Author affiliations: Melbourne Sexual Health Centre, Alfred Health, Carlton, Victoria, Australia (T.R.H. Read, C.K. Fairley, M. Grant, E.P.F. Chow, K. Worthington, C.S. Bradshaw); Monash University, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia (T.R.H. Read, C.K. Fairley, G.L. Murray, E.P.F. Chow, C.S. Bradshaw); Statens Serum Institut, Copenhagen, Denmark (J.S. Jensen); Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, Parkville, Victoria, Australia (J.A. Danielewski, J. Su, G.L. Murray, S.M. Garland, S.N. Tabrizi); Royal Women’s Hospital, Parkville (J.A. Danielewski, J. Su, G.L. Murray, S.M. Garland, S.N. Tabrizi); University of Melbourne, Parkville (S.M. Garland, S.N. Tabrizi, C.S. Bradshaw)
Main Article
Figure 2
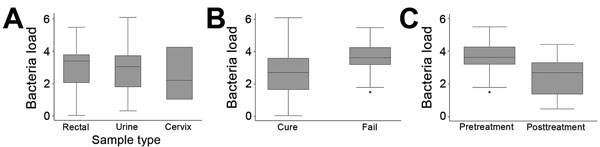
Figure 2. Mycoplasma genitalium bacterial loads (log10) and treatment outcomes, Melbourne Sexual Health Centre, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 2012–2016. A) M. genitalium load compared in urine (n = 67), rectal swab (n = 26), and cervical swab (n = 3) samples. For urine vs. rectal samples, p = 0.56; for urine vs. cervical samples, p = 0.70. B) Comparison of pretreatment M. genitalium loads in infections not cured (n = 26) and cured (n = 71) by pristinamycin. p<0.01. C) Comparison of M. genitalium loads in pretreatment and posttreatment samples from cases in which pristinamycin failed (n = 26). p<0.001..Box plots indicate 25th percentile (bottom of box), 75th percentile (top of box), median (horizontal line within box), and range (whiskers). Dots represent outlying individual observations.Dots under the error bars indicate individual outliers.
Main Article
Page created: January 17, 2018
Page updated: January 17, 2018
Page reviewed: January 17, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
