Volume 24, Number 2—February 2018
CME ACTIVITY - Synopsis
Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in Cryptogenic Liver Abscesses, Paris, France
Figure 2
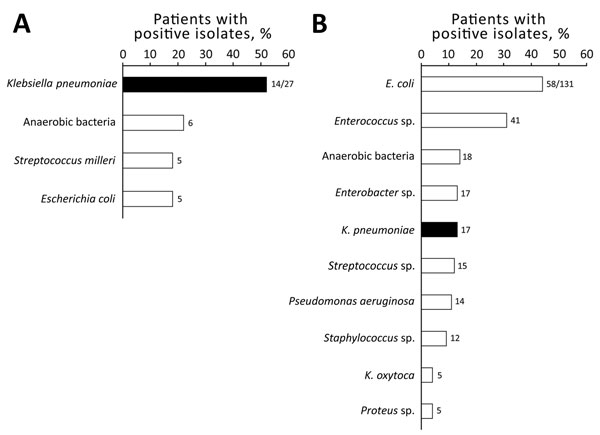
Figure 2. Bacteria isolated from patients with A) cryptogenic (n = 27) and B) noncryptogenic (n = 131) liver abscesses, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France, 2010−2015. Black bars indicate Klebsiella pneumoniae. Values above bars indicate number of isolates. Differences for each bacterial species between cryptogenic and noncryptogenic abscesses were statistically significant for K. pneumoniae (p = 0.00005), Enterococcus species (p = 0.0001), Staphylococcus species (p = 0.0009), and Enterobacter species (p = 0.05). Five (18%) of 27 cryptogenic abscesses were polymicrobial, and 63 (48%) of 131 noncryptogenic abscesses were polymicrobial. Enterococcus species isolates were mainly E. faecalis (21 isolates) and E. faecium (21 isolates). For Streptococcus species isolates, 13/15 were S. milleri. Staphylococcus aureus represented 5 (42%) of 12 Staphylococcus species isolates.