Volume 24, Number 3—March 2018
Dispatch
Severe Pneumonia Caused by Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans Infection, Japan
Figure 2
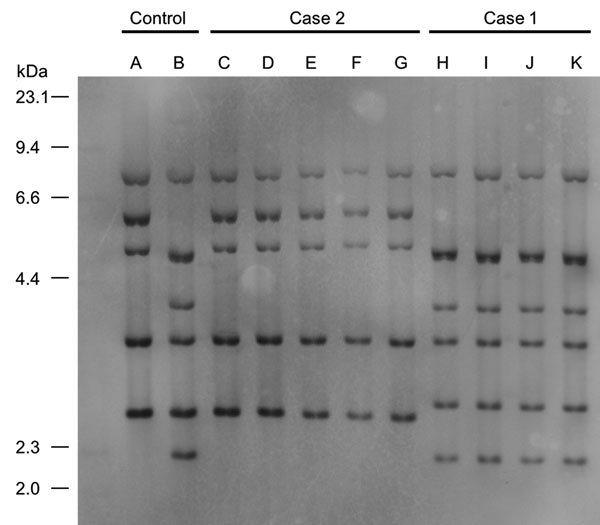
Figure 2. Figure 2. Ribotyping tests for isolates from 2 case-patients with severe pneumonia caused by Corynebacterium ulcerans infection, Japan. Case-patient 1 isolate was categorized as R3 group and case-patient 2 isolate as R1 group. A, 0102 (R1 group); B, 0211 (R4 group); C, isolate from case-patient 2’s exudate on bronchus; D, isolate from cat 1’s throat in case 2; E, isolate from cat 2’s nasal cavity in case 2; F, isolate from cat 2’s throat in case 2; G, isolate from cat 2’s conjunctiva in case 2; H, isolate from case-patient 1’s exudate on bronchus; I, isolate from cat’s feeding tray in case-patient 1’s house; J, isolate from cat’s blanket in case-patient 1’s house; K, isolate from telephone receiver in case-patient 1’s house.
Page created: February 16, 2018
Page updated: February 16, 2018
Page reviewed: February 16, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.