Volume 24, Number 4—April 2018
Research
Evolution of Sequence Type 4821 Clonal Complex Meningococcal Strains in China from Prequinolone to Quinolone Era, 1972–2013
Figure 1
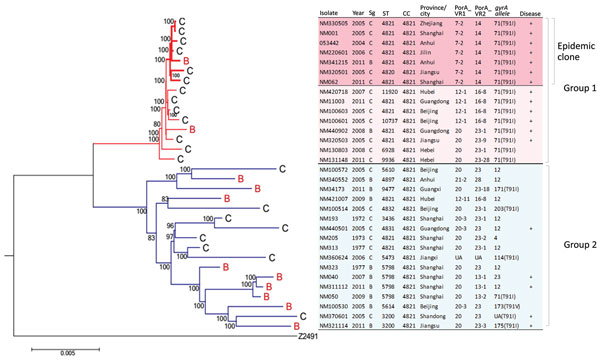
Figure 1. Core genome phylogenetic tree showing relationships between Neisseria meningitidis serogroups C and B CC4821 strains, China, 1972–2011. The strains cluster within 1 of 2 distinct phylogenetic groups, group 1 and group 2. Within group 1 is an antigenically distinct clonal group (epidemic clone) containing outbreak-associated strains. Tree is rooted using serogroup A reference strain (Z2491) as an outgroup. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic trees of aligned core genome sequences were generated under a general time reversible model of evolution with gamma rate heterogeneity, with 1,000 rapid bootstrap replicates represented as a percentage. Only node labels with >80% bootstrap support are shown. Strain type and date and place of isolation are shown; + indicates strains isolated from invasive disease cases. Resistant point mutations on the T91 position of gyrA gene are shown alongside data on gyrA allele designation. Scale bar represents total substitutions per site. CC, clonal complex; PorA VR, outer membrane protein PorA variable regions; Sg, serogroup; ST, sequence type.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.