Volume 24, Number 4—April 2018
Dispatch
Novel Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N6) Virus in the Netherlands, December 2017
Figure 2
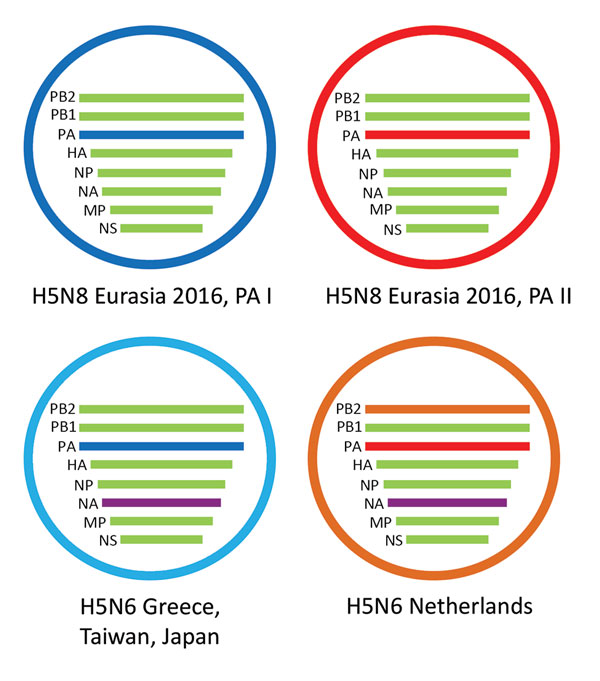
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the HPAI H5N6 reassortant virus detected in the Netherlands. Two variants of HPAI H5N8 were detected in 2016; they have different PA gene segments, called PA I and PA II. The novel virus evolved from H5N8 viruses having a PA II gene segment, but obtained both novel NA and PB2 gene segments. The H5N6 viruses detected in Greece, Japan, and Taiwan have evolved from H5N8 viruses that have a PA I gene segment and have an N6 segment similar to the virus detected in the Netherlands. HPAI, highly pathogenic avian influenza; PB, polymerase basic; PA, polymerase acidic; HA, hemagglutinin; NP, nucleoprotein; NA, neuraminidase; MP, matrix protein; NS, nonstructural protein.
Page created: March 19, 2018
Page updated: March 19, 2018
Page reviewed: March 19, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.