Volume 24, Number 5—May 2018
Dispatch
Second Human Pegivirus in Hepatitis C Virus–Infected and Hepatitis C Virus/HIV-1–Co-infected Persons Who Inject Drugs, China
Figure 2
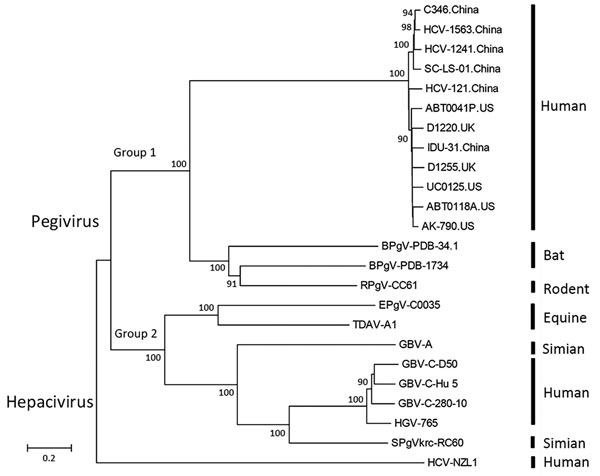
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of second human pegivirus (HPgV-2) isolates identified in our study (China) and abroad (UK and US). Phylogenetic trees of nucleotide sequences from complete sequences of HPgV-2 strains isolated in our study and elsewhere as well as hepatitis C virus and pegivirus strains from humans, simians, equids, bats, and rodents are included. The phylogenetic trees were constructed with the neighbor-joining tree method using MEGA6 software (http://www.megasoftware.net). Bootstrap analysis with 1,000 replicates was performed to determine the robustness of branching; values are shown on branches. Scale bar indicates the estimated number of nucleotide substitutions per site. The near full-length genome sequences of HPgV-2 identified in this study have been submitted to GenBank under accession numbers KX528230 (HCV-121), KX528231 (IDU31), KY971606 (C346), MG457178 (SC-LS-01), MF770985 (HCV1241), and MF770986 (HCV1563). UK, United Kingdom; US, United States.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.