Volume 24, Number 7—July 2018
Dispatch
Use of Urea Wash ELISA to Distinguish Zika and Dengue Virus Infections
Figure 1
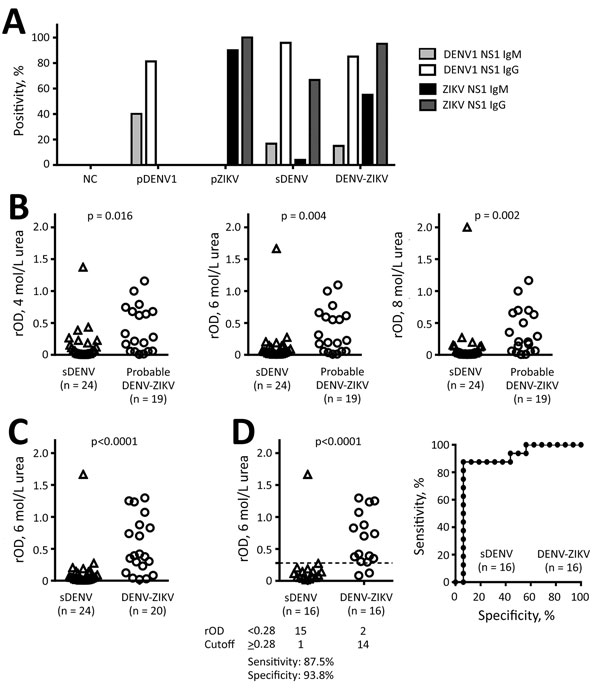
Figure 1. NS1 IgM and IgG ELISAs and urea wash in ZIKV–NS1 IgG ELISA. A) Positivity rates for each panel. Only samples collected <3 months after symptom onset were tested for IgM. B) sDENV infection and probable DENV-ZIKV panels were tested with different concentrations (4, 6, and 8 mol/L) of urea wash. C, D) sDENV and DENV-ZIKV panels were tested with 6 mol/L urea wash: C) all samples; D) samples positive for both DENV-1–NS1 and ZIKV-NS1 IgG ELISAs. Sensitivity and specificity are based on relative optical density cutoff at 0.28 (dashed line). Receiver-operating characteristics are shown in the graph on the right. Data are the mean of 2 experiments (each in duplicate). The 2-tailed Mann-Whitney test was used. DENV, dengue virus; DENV-ZIKV, confirmed Zika virus infection with previous exposure to DENV; NS1, nonstructural protein 1; pDENV1, primary DENV-1 infection; pZIKV, primary ZIKV infection; rOD, relative optical density; sDENV, secondary DENV infection; ZIKV, Zika virus.