Zika Virus Seropositivity in 1–4-Year-Old Children, Indonesia, 2014
R. Tedjo Sasmono

, Rama Dhenni, Benediktus Yohan, Paul Pronyk, Sri Rezeki Hadinegoro, Elizabeth Jane Soepardi, Chairin Nisa Ma’roef, Hindra I. Satari, Heather Menzies, William A. Hawley, Ann M. Powers, Ronald Rosenberg, Khin Saw Aye Myint, and Amin Soebandrio
Author affiliations: Eijkman Institute for Molecular Biology, Jakarta, Indonesia (R.T. Sasmono, R. Dhenni, B. Yohan, C.N. Ma’roef, K.S.A. Myint, A. Soebandrio); UNICEF Indonesia, Jakarta (P. Pronyk); University of Witwatersrand School of Public Health, Johannesburg, South Africa (P. Pronyk); Universitas Indonesia Medical School, Jakarta (S.R. Hadinegoro, H.I. Satari); Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital, Jakarta (S.R. Hadinegoro, H.I. Satari); Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia, Jakarta (E.J. Soepardi); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, USA (H. Menzies, W.A. Hawley); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA (A.M. Powers, R. Rosenberg)
Main Article
Figure
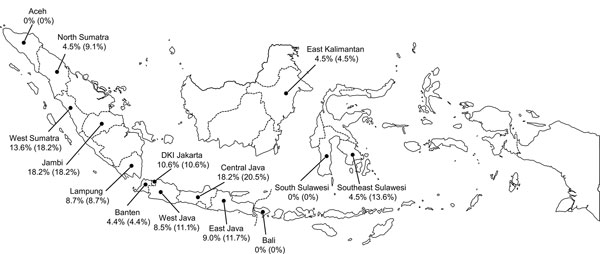
Figure. Geographic distribution of Zika virus–seropositive 1−4-year-old children, Indonesia, October–November, 2014. The values listed for each province indicate the percentage of serum samples confirmed Zika virus seropositive (percentage serum samples suspected to be Zika virus seropositive). Samples suspected to be Zika virus positive were those that were positive on initial Zika virus PRNT90 (plaque reduction neutralization test with neutralization defined as >90% reduction in challenge virus PFUs) screening when using a 1:10 serum sample dilution. Serum samples confirmed as Zika virus seropositive were those that neutralized Zika virus only or had a PRNT90 titer for Zika virus that was >4-fold higher than the PRNT90 titer for any DENV.
Main Article
Page created: August 15, 2018
Page updated: August 15, 2018
Page reviewed: August 15, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
