Volume 25, Number 11—November 2019
Research Letter
Molecular Epidemiology of Hantaviruses in the Czech Republic
Figure
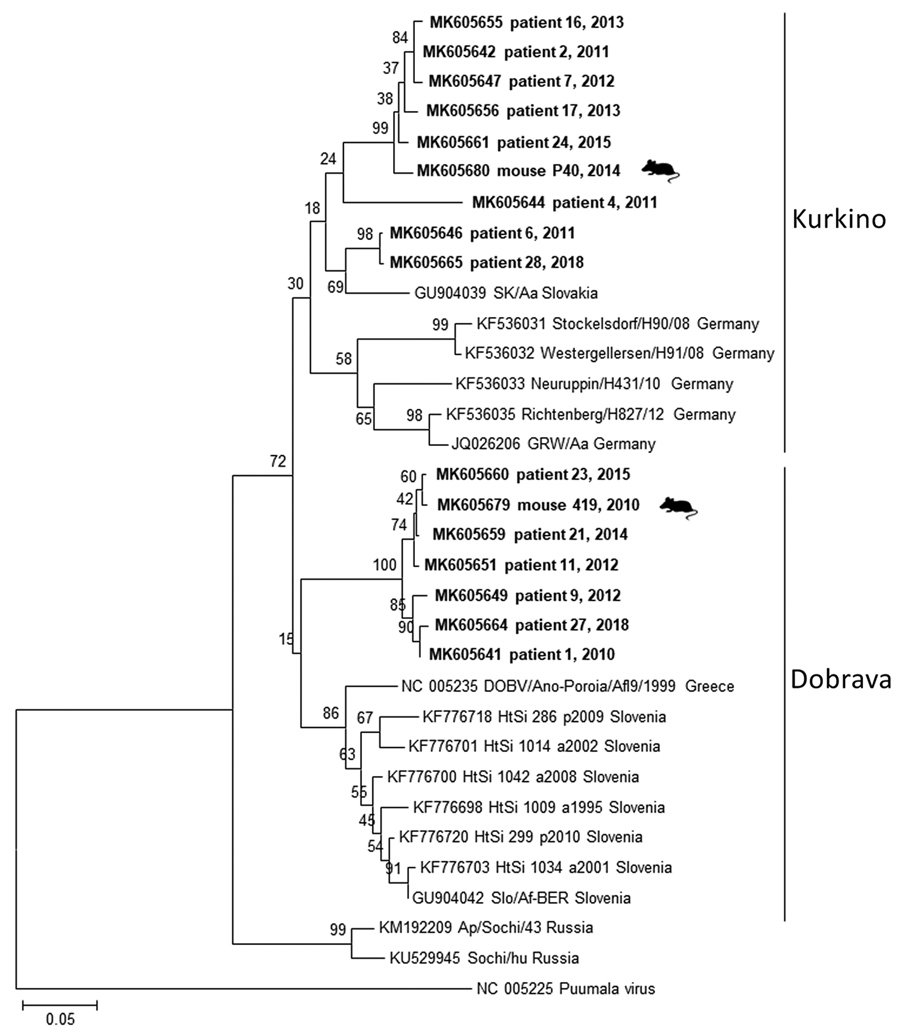
Figure. Phylogenetic tree constructed with partial 195-bp fragments of the DOBV large segment from humans and mice, Czech Republic, 2010–2018. Sequences from this study (bold) were compared with available sequences from the GenBank database; patient numbers are provided, and mouse samples are labeled. Samples with sequences identical to another sample were excluded for simplification purposes. Sequences were aligned with BioEdit (9), and the phylogenetic tree was prepared by using MEGA 7.0 (https://megasoftware.net) and the neighbor-joining method. Analyses were performed with the Jukes-Cantor model by using a gamma distribution with 5 rate categories and a bootstrap value of 1,000. The genotype clusters are labeled. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. The Puumala virus sequence was used as an outgroup. DOBV, Dobrava-Belgrade virus.
References
- Olsson GE, Leirs H, Henttonen H. Hantaviruses and their hosts in Europe: reservoirs here and there, but not everywhere? Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010;10:549–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Klempa B, Avsic-Zupanc T, Clement J, Dzagurova TK, Henttonen H, Heyman P, et al. Complex evolution and epidemiology of Dobrava-Belgrade hantavirus: definition of genotypes and their characteristics. Arch Virol. 2013;158:521–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pejcoch M, Kríz B. Hantaviruses in the Czech Republic. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:756–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Papa A, Zelená H, Barnetová D, Petrousová L. Genetic detection of Dobrava/Belgrade virus in a Czech patient with Haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16:1187–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zelena H, Zvolankova V, Zuchnicka J, Liszkova K, Papa A. Hantavirus infection during a stay in a mountain hut in Northern Slovakia. J Med Virol. 2011;83:496–500. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zelená H, Rumlerová M, Kodras K, Beroušková P, Mrázek J, Smetana J. [Hantavirus causing fatal haemorrhagic fever in the Czech Republic] [in Czech]. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2017;66:149–52.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Státní Zdravotní Ústav. Cases of selected infectious diseases in the Czech Republic, January–July 2019. 2019 [cited 2019 Sep 10]. http://szu.cz/publikace/data/2019/vyskyt-vybranych-hlasenych-infekci-v-ceske-republice-leden-1?lang=1
- Klempa B, Fichet-Calvet E, Lecompte E, Auste B, Aniskin V, Meisel H, et al. Hantavirus in African wood mouse, Guinea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:838–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hall TA. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1999;41:95–8.
- Sibold C, Ulrich R, Labuda M, Lundkvist A, Martens H, Schütt M, et al. Dobrava hantavirus causes hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in central Europe and is carried by two different Apodemus mice species. J Med Virol. 2001;63:158–67. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar