Volume 25, Number 6—June 2019
Research Letter
Molecular Evidence of Human Monkeypox Virus Infection, Sierra Leone
Figure
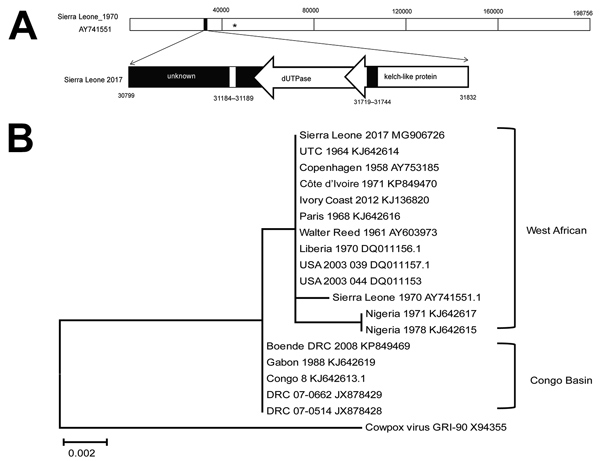
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis and molecular signatures of monkeypox virus (MPXV) Sierra Leone 2017 and other collected MPXV isolates. A) Schematic representation of the MPXV Sierra Leone 2017 genomic fragment by reference to genomic data on MPXV Sierra Leone 1970. MPXV Sierra Leone 2017 contains 3 parts: an unknown region, genes encoding dUTPase, and genes encoding partial kelch-like protein. *, binding position of primers used for real-time PCR detection. Bottom panel displays genes described. Arrows indicate direction of transcription. B) Phylogenetic relationships between genomic fragments of MPXV collected in Sierra Leone and other orthopoxviruses. Neighbor-joining phylograms constructed by using MEGA6 (https://www.megasoftware.net) and the maximum-likelihood method. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.