Volume 25, Number 7—July 2019
Research
Nationwide Stepwise Emergence and Evolution of Multidrug-Resistant Campylobacter jejuni Sequence Type 5136, United Kingdom
Figure 3
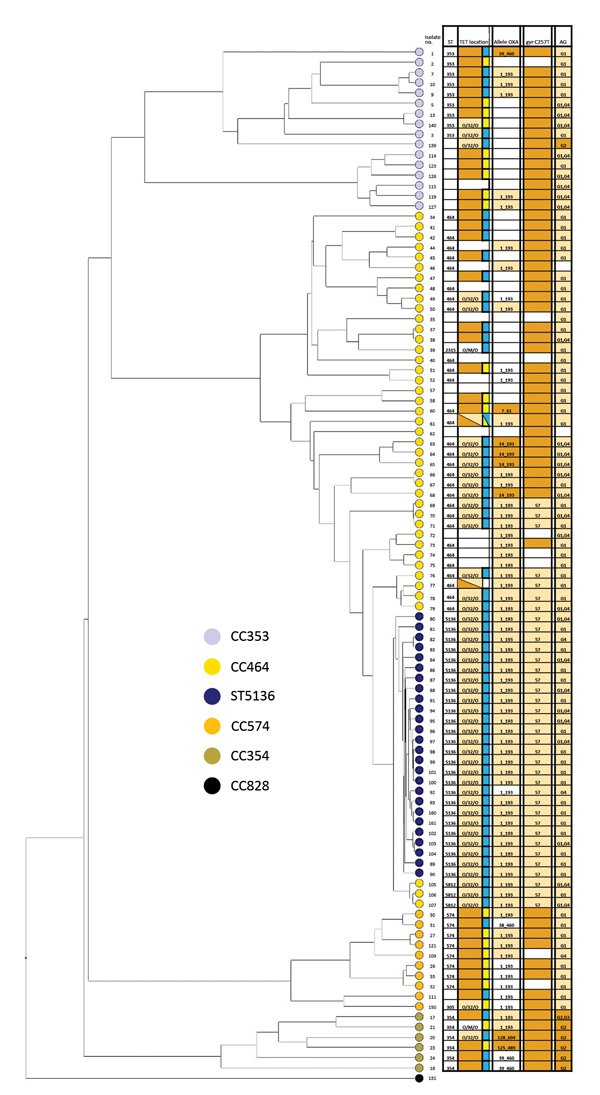
Figure 3. Whole-genome multilocus sequence typing of 100 selected isolates of Campylobacter jejuni from CC464, CC353, CC354, and CC574, Scotland. The tree was constructed using the UPGMA algorithm based on locus similarity. Isolate ID number indicated at branch end is linked to metadata in Appendix Table 2. Light orange boxes in the grid indicate variants associated with ST5136 isolates spread across the phylogeny; dark orange boxes denote resistance in individual isolates. Blue boxes represent tetracycline resistance in chromosome; yellow boxes, in plasmid. AG, aminoglycoside; CC, clonal complex; ID, identification; OXA, oxacillin; ST, sequence type; TET, tetracycline.
Page created: June 17, 2019
Page updated: June 17, 2019
Page reviewed: June 17, 2019
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.